Introduction
Tyson Foods, Inc. is one of the world’s largest food companies and a leading processor and marketer of chicken, beef, and pork. Founded in 1935, the company has grown into a global food powerhouse with a significant presence in the United States and abroad. This report provides a detailed examination of Tyson Foods’ history, growth strategies, business operations, competitive positioning, and the challenges it faces in the modern food industry.
History and Early Growth
Founding and Early Years (1935-1950s)
Tyson Foods was founded in 1935 by John W. Tyson in Springdale, Arkansas, during the Great Depression. Initially, the company focused on transporting chickens from Arkansas to markets in the Midwest. As demand for poultry grew, Tyson expanded its operations to include poultry processing, marking the beginning of its vertical integration strategy.
Expansion and Industry Leadership (1960s-1980s)
In the 1960s, Tyson Foods introduced innovations in poultry farming, feed production, and distribution. By acquiring processing plants and hatcheries, the company gained control over the entire production cycle. Tyson went public in 1963, which provided capital to fund expansion. During the 1970s and 1980s, Tyson acquired several regional poultry businesses, further solidifying its dominance in the industry.
Diversification and Global Expansion (1990s-2000s)
By the 1990s, Tyson Foods began diversifying beyond poultry. The acquisition of Hudson Foods in 1998 and the blockbuster $3.2 billion purchase of IBP, Inc. in 2001 brought Tyson into the beef and pork markets, making it the largest meat processor in the United States. The acquisition of meat processors outside the U.S. further expanded its global footprint.
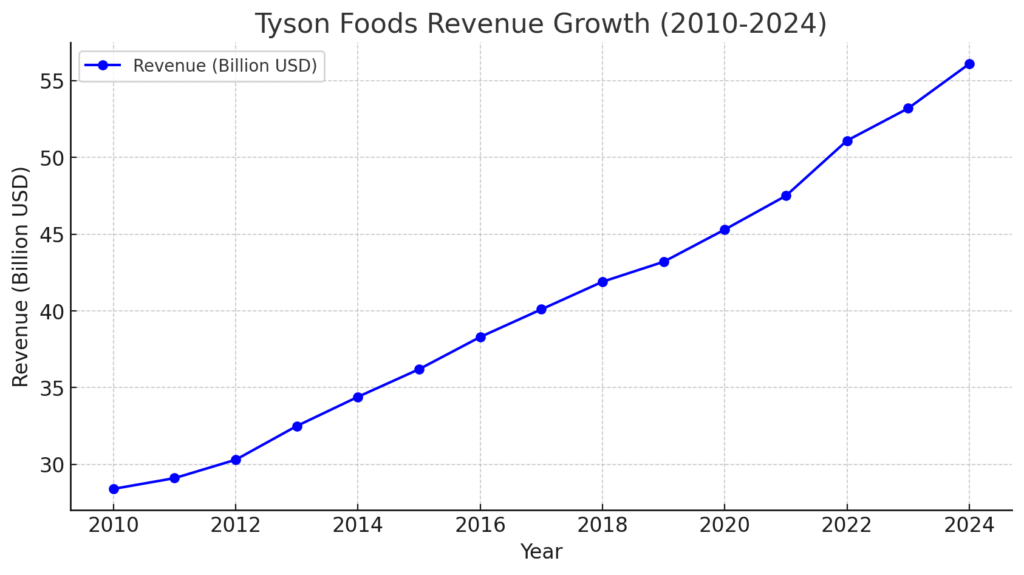
Recent Developments and Innovation (2010-Present)
In recent years, Tyson Foods has focused on sustainability, alternative proteins, and digital transformation. The company has invested in plant-based and lab-grown meat startups, launched new product lines, and adopted automation technologies to improve efficiency. Despite these advancements, Tyson continues to face significant regulatory and operational challenges.
Business Strategy and Competitive Edge
Vertical Integration
One of Tyson Foods’ key strategies is vertical integration, which allows the company to control the entire production chain, from breeding and feed production to processing and distribution. This model has enabled Tyson to optimize costs, maintain quality, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Brand Portfolio and Market Positioning
Tyson owns a diverse portfolio of brands, including Tyson, Jimmy Dean, Hillshire Farm, Ball Park, and State Fair. These brands cater to various consumer preferences, from frozen and processed meats to premium and organic options. By leveraging its strong brand recognition, Tyson has remained a dominant player in the food industry.
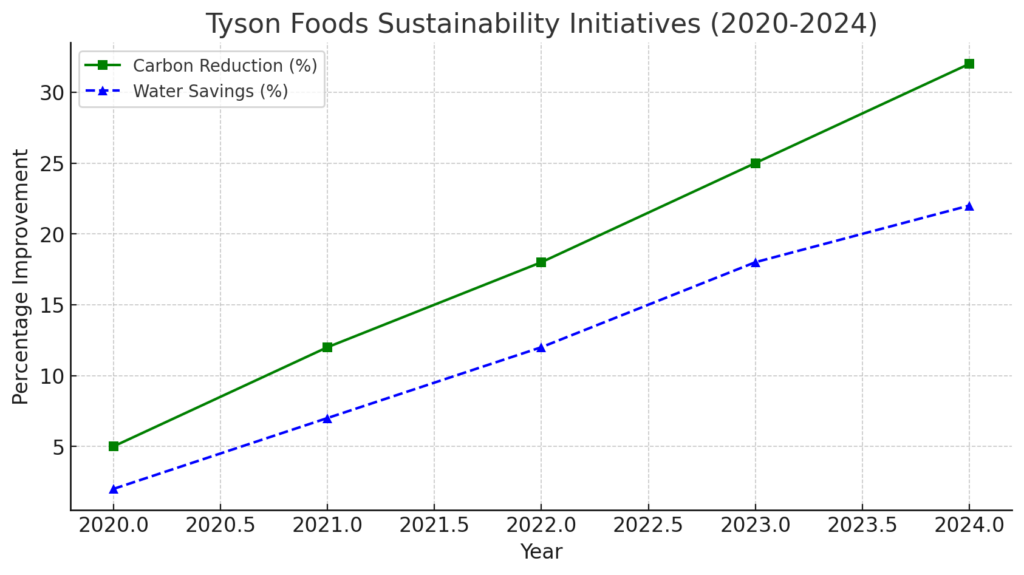
Sustainability Initiatives
To address environmental concerns, Tyson Foods has committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, improving water and energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable farming practices. The company has set ambitious sustainability goals, such as achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 and sourcing responsibly-raised livestock.
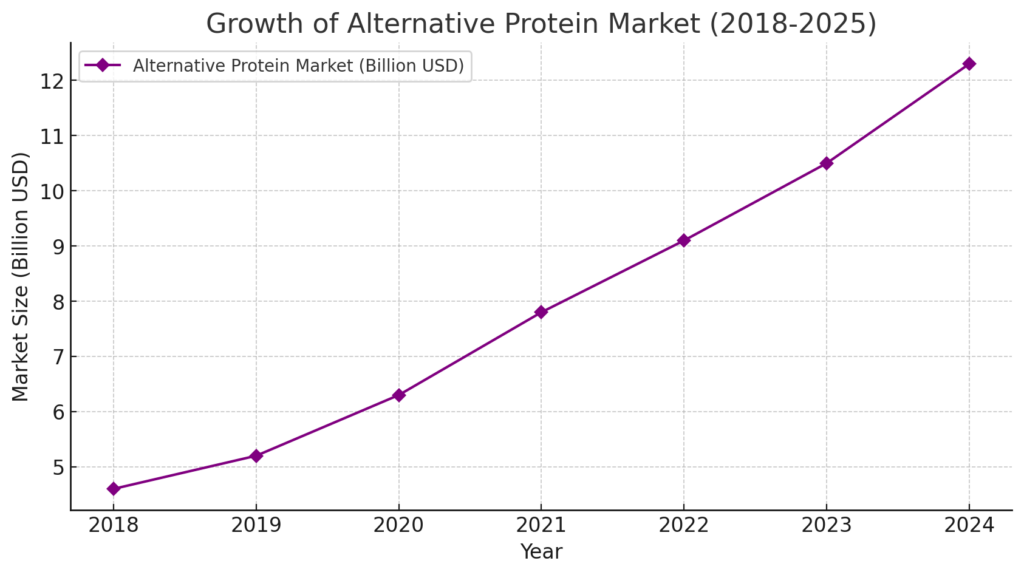
Investment in Alternative Proteins
Recognizing the rise of plant-based diets and alternative proteins, Tyson has invested in companies like Beyond Meat and developed its own line of plant-based products under the Raised & Rooted brand. This strategic move positions Tyson to compete in the growing alternative protein market.
Challenges and Controversies
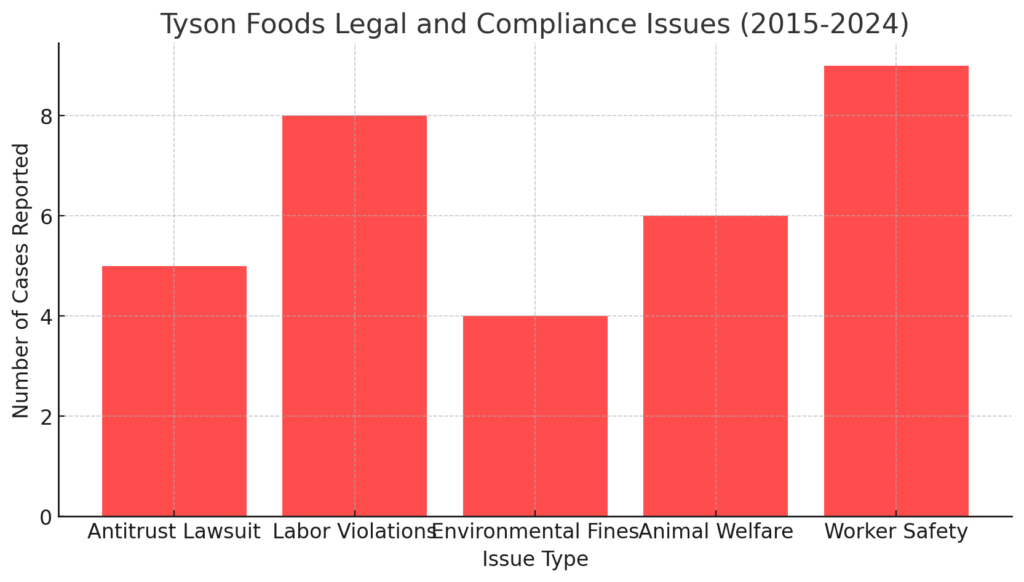
Labor Issues
Tyson Foods has faced multiple labor-related controversies, including allegations of poor working conditions, wage disputes, and inadequate protections for workers. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Tyson came under scrutiny for failing to implement sufficient safety measures in its meatpacking plants, leading to widespread outbreaks among employees.
Environmental and Animal Welfare Concerns
As a leading meat processor, Tyson has been criticized for its environmental impact, including greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and deforestation linked to feed production. Additionally, animal welfare organizations have accused the company of inhumane treatment of livestock, prompting Tyson to adopt stricter animal welfare policies.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, have impacted Tyson’s operations. Rising feed costs, transportation bottlenecks, and labor shortages have posed significant challenges to maintaining stable production levels and profitability.
Legal and Regulatory Issues
Tyson Foods has faced multiple legal battles, including antitrust lawsuits alleging price-fixing in the chicken industry. Regulatory scrutiny has intensified, with governments imposing stricter compliance requirements related to food safety, labor laws, and environmental impact.
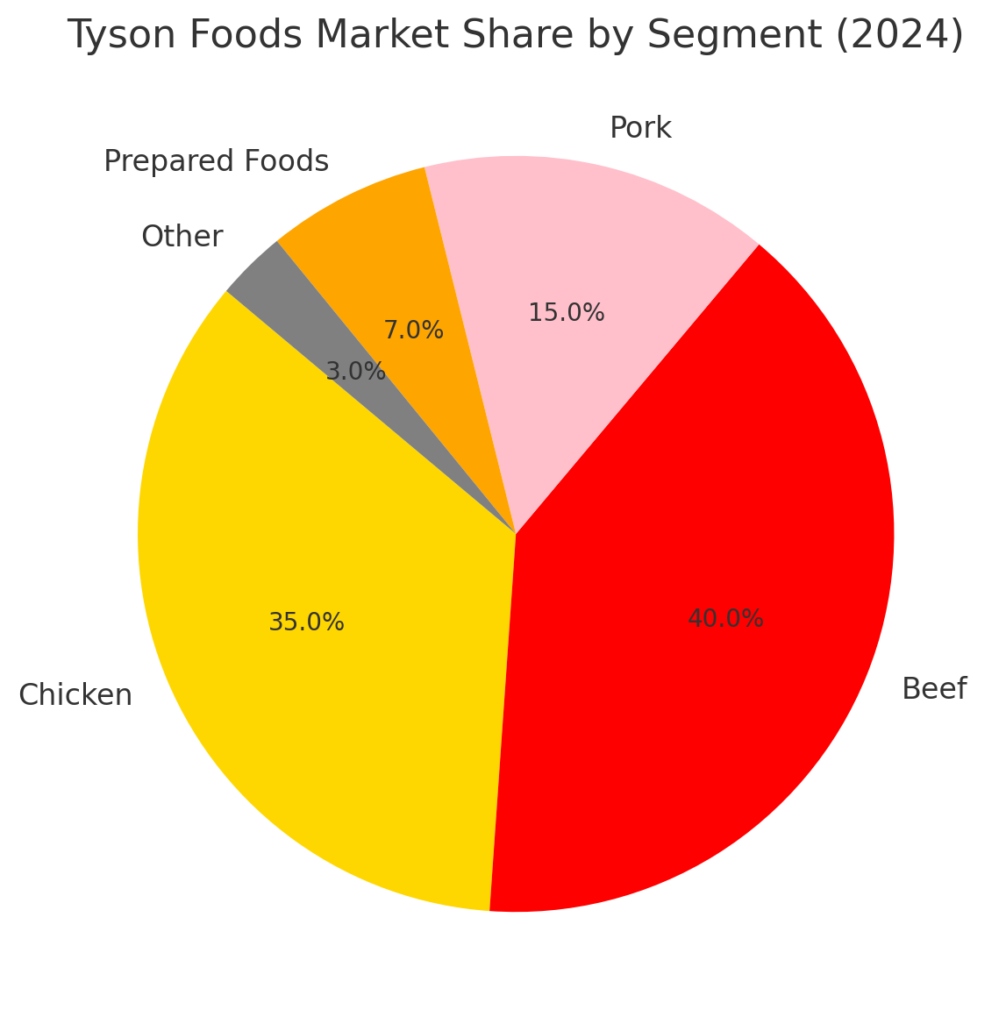
Financial Performance and Market Outlook
Despite its challenges, Tyson Foods has maintained strong financial performance. The company generates annual revenues exceeding $50 billion, driven by consistent demand for meat products. However, rising input costs and changing consumer preferences present ongoing risks. Tyson continues to explore new growth opportunities, such as international expansion and product innovation, to sustain its market leadership.
Conclusion
Tyson Foods’ journey from a small poultry transportation business to a global meat-processing giant reflects its ability to adapt and innovate. The company’s vertical integration, strong brand portfolio, sustainability efforts, and investment in alternative proteins have positioned it well in the evolving food industry. However, ongoing labor, environmental, and regulatory challenges require continuous strategic adjustments. As Tyson navigates these complexities, its future success will depend on its ability to balance profitability with ethical and sustainable business practices.
Sources:
- Tyson Foods Official Website
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission – Tyson Foods
- Reuters – Tyson Foods News
- Bloomberg – Tyson Foods
- CNN Business – Tyson Foods