
Introduction
Lemons (Citrus limon) are one of the most widely cultivated citrus fruits in the world, with a high demand due to their culinary, medicinal, and industrial applications. The global lemon industry plays a crucial role in international trade, providing key economic contributions to various countries, especially in warm and tropical regions. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global lemon industry, including production, trade, market trends, and challenges facing the sector.
1. Global Production of Lemons
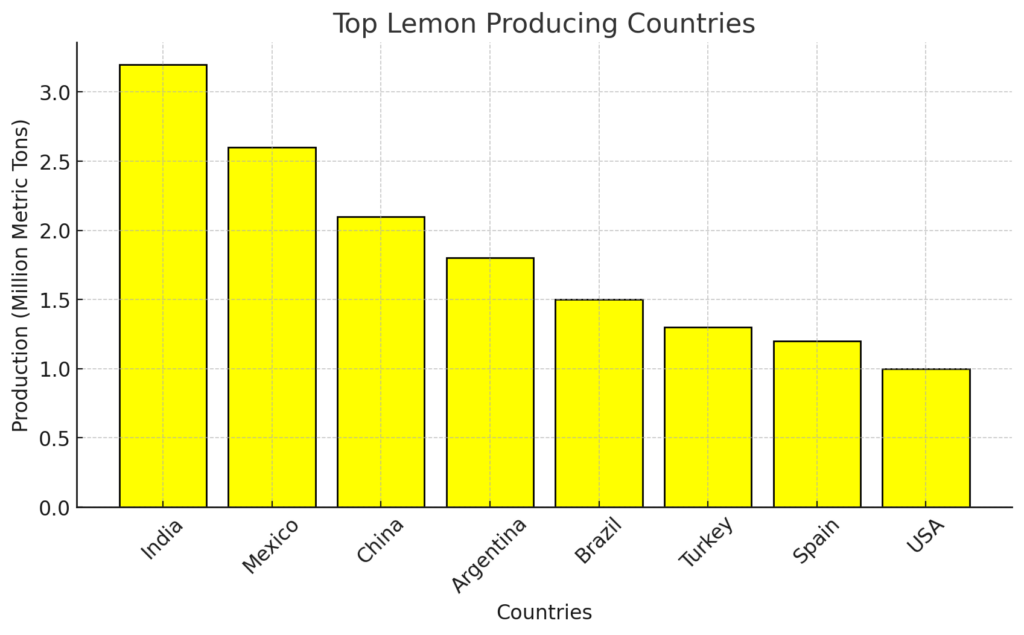
1.1 Leading Lemon Producing Countries
Lemon production is concentrated in a few key regions with optimal growing conditions. The top lemon-producing countries include:
- India – The largest producer of lemons, accounting for nearly 20% of global production.
- Mexico – A major supplier for both domestic consumption and export.
- China – A significant player, producing lemons primarily for the domestic market.
- Argentina – The leading exporter of lemons, known for its high-quality produce.
- Brazil – A growing force in lemon production, supplying both local and international markets.
- Turkey, Spain, and the United States – Major producers, especially for European and North American markets.
1.2 Lemon Production by Region
- Asia: India and China dominate production, while Pakistan and Iran also contribute significantly.
- South America: Argentina and Brazil lead, with Chile increasing its output.
- Europe: Spain and Italy are the largest producers, catering to European markets.
- North America: The United States (mainly California) and Mexico are key suppliers.
- Africa: South Africa is an emerging player in the global lemon industry.
- Oceania: Australia grows lemons primarily for domestic consumption and exports to Asia.
2. The Global Lemon Trade
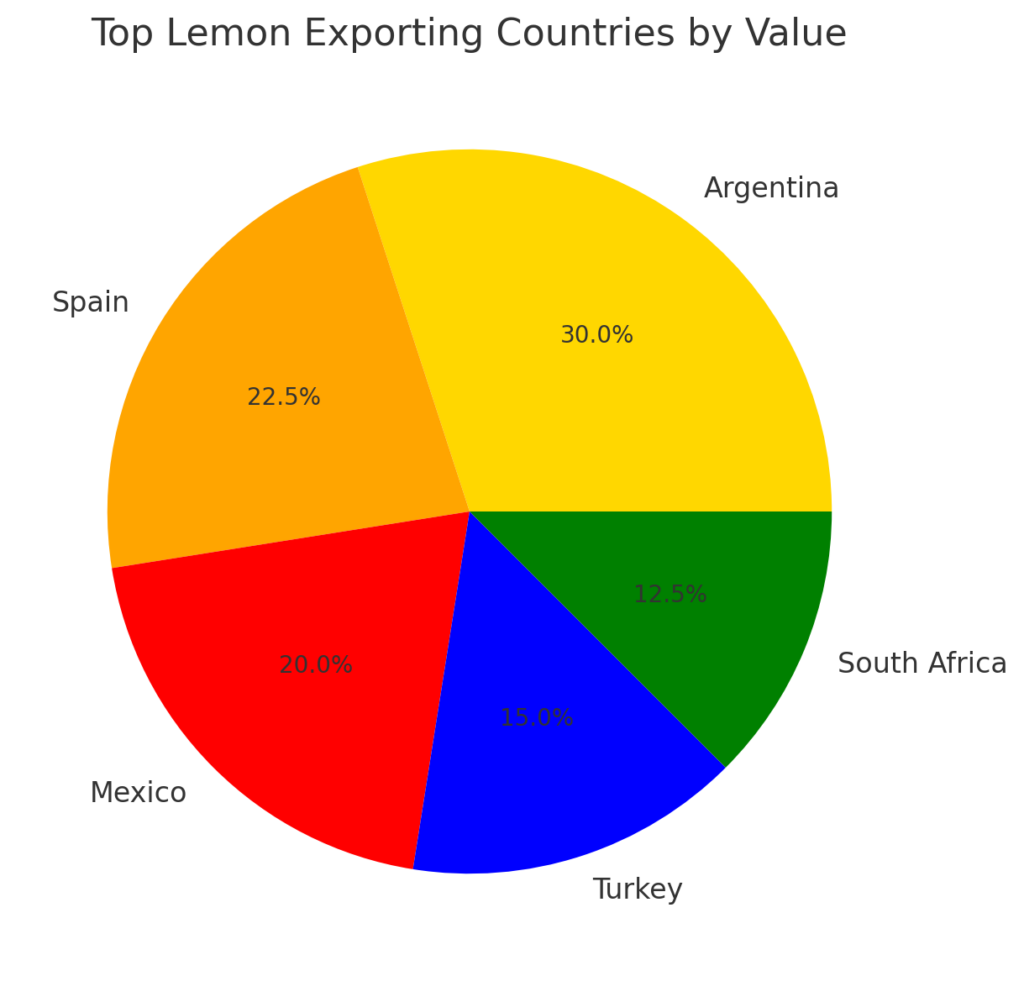
2.1 Leading Lemon Exporting Countries
- Argentina – The world’s largest exporter, shipping lemons to Europe, the US, and Asia.
- Spain – A dominant supplier to the European Union.
- Mexico – A leading exporter to the US and Canada.
- Turkey – Supplies Middle Eastern and European markets.
- South Africa – An emerging exporter to Europe and Asia.
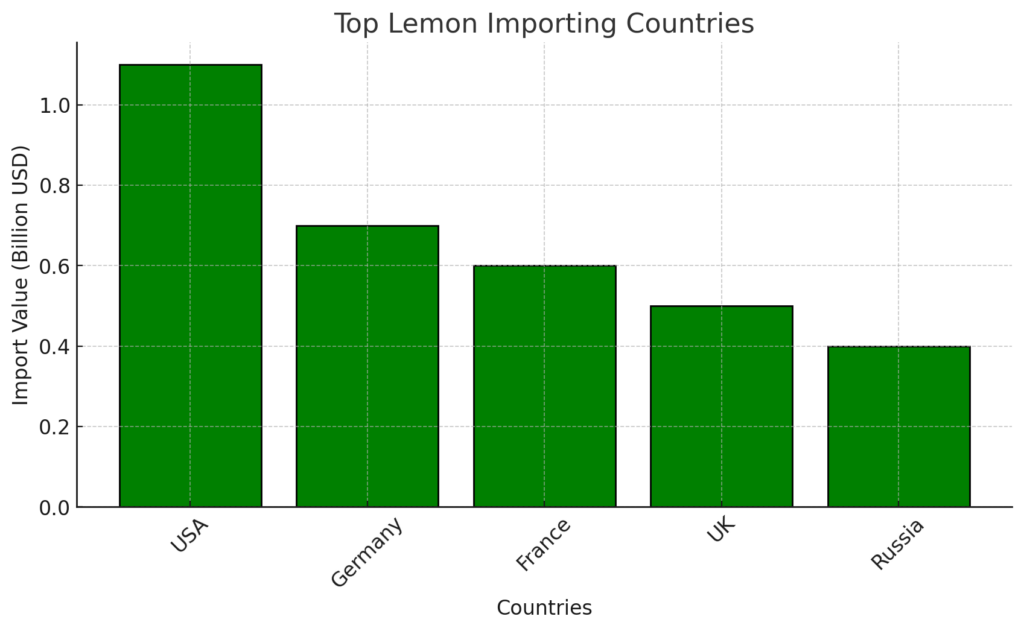
2.2 Major Lemon Importing Countries
- United States – The largest importer, relying on Mexico and Argentina.
- Germany, France, and the UK – Key European importers.
- Russia – A growing market for lemon imports from Turkey and Argentina.
- China and Japan – Increasing lemon imports, especially from South America.
- Middle Eastern countries – Significant demand for lemons from Turkey and South Africa.
2.3 Lemon Pricing and Market Fluctuations
Lemon prices fluctuate based on seasonality, climate conditions, and international trade policies. For example, droughts or citrus diseases can cause supply shortages, increasing prices globally. Conversely, bumper crops can lead to oversupply and reduced prices.
3. Lemon Processing Industry
3.1 Lemon Products and Their Market Demand
Lemons are processed into various products, including:
- Lemon Juice – Used in beverages, food preparation, and health drinks.
- Lemon Oil – An essential component in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and cleaning products.
- Lemon Zest and Peel – Used in flavoring food products.
- Lemon-Based Beverages – An expanding segment in the global market.
- Lemon Concentrates – Widely used in food manufacturing and flavoring industries.
3.2 Lemon-Based Industries
The demand for lemon-derived products spans across multiple industries, such as:
- Food & Beverage – The largest consumer of lemon juice, zest, and flavoring.
- Cosmetics & Personal Care – Utilizing lemon oil for skincare and haircare products.
- Pharmaceuticals – Using lemon extracts for medicinal applications.
- Cleaning & Household Products – Leveraging lemon oil’s natural disinfectant properties.
4. Challenges Facing the Lemon Industry
4.1 Climate Change and Weather Conditions
Lemon cultivation is highly susceptible to weather conditions, including:
- Droughts – Reducing yields in major producing regions like Argentina and California.
- Frost – Causing production losses, especially in European lemon-growing areas.
- Storms and Floods – Impacting citrus groves, leading to reduced quality and supply.
4.2 Pests and Diseases
- Citrus Canker – A bacterial disease affecting lemon quality.
- Huanglongbing (HLB) or Citrus Greening – A devastating disease that has affected lemon orchards worldwide.
- Fruit Flies and Aphids – Common pests that can lead to crop loss.
4.3 Trade Barriers and Tariffs
Countries impose tariffs and regulations that affect lemon exports. For example:
- EU Import Regulations – Strict pesticide residue standards impact exporters.
- US Tariffs on Imports – Affect Mexican and Argentine lemon shipments.
- China’s Trade Policies – Can affect lemon import trends from Western countries.
4.4 Supply Chain Disruptions
- Shipping Delays – Affecting fresh lemon exports.
- Cold Storage Costs – Rising expenses in maintaining lemon quality.
- Labor Shortages – Impacting harvesting and processing efficiency.
5. Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
5.1 Growth of Organic and Sustainable Lemon Farming
Consumers are demanding organic lemons free from pesticides, leading to:
- Expansion of Organic Lemon Farms – Countries like Spain and the US are increasing organic production.
- Sustainable Farming Practices – Reduced water usage, organic fertilizers, and better pest management techniques.
5.2 Technological Advancements in Lemon Farming
- Precision Agriculture – Using AI and drones to monitor lemon crops.
- Genetic Improvements – Developing disease-resistant lemon varieties.
- Automated Harvesting Techniques – Enhancing efficiency in large lemon farms.
Conclusion
The global lemon industry continues to thrive, with increasing production, trade, and demand across multiple sectors. However, the industry faces challenges such as climate change, pest infestations, and trade regulations. By embracing technology, sustainable farming, and new market opportunities, the lemon sector is set for future growth. Countries investing in innovation and sustainability will lead the way in supplying high-quality lemons to global consumers.
Sources:
- https://www.fao.org
- https://www.trademap.org
- https://www.statista.com
- https://www.cbi.eu
- https://www.agrifarming.in
