Introduction
India is one of the largest producers of corn (maize) in the world, with the crop being vital to both the country’s food security and agricultural economy. Corn plays an essential role in India’s agricultural output, serving various sectors including food, animal feed, and industrial uses like starch production and biofuel manufacturing. With favorable climatic conditions in several regions of India and a growing demand for maize, India’s corn industry has expanded considerably over the past few decades.
In this report, we will provide an in-depth look at the corn industry in India, covering key production areas, the companies driving growth, challenges faced by the sector, and future opportunities. We will also explore how India is positioned in the global corn market and the potential for increased domestic production and exports.
Importance of Corn in India’s Agriculture
Corn is one of the staple crops in India, second only to rice in terms of production. While maize is grown in many parts of the country, it is especially important in states like Karnataka, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh. Corn contributes significantly to India’s agricultural GDP and is used in a wide array of applications.
The major uses of corn in India include:
- Human Consumption: Corn is used for direct consumption, particularly in the form of cornmeal and popcorn, and is a staple in several regions of the country.
- Animal Feed: With the growing livestock sector in India, corn is one of the main ingredients in animal feed, especially for poultry and cattle farming.
- Industrial Uses: Corn is used in producing starch, ethanol, and other industrial products, contributing to India’s biofuel sector and food processing industry.
In addition to being an essential food crop, corn also supports India’s growing biofuels industry. With the government’s push for green energy solutions, the demand for maize for ethanol production is increasing, adding another layer of economic importance to the crop.
Key Corn-Producing Regions in India
India’s diverse climate allows for maize to be grown across a wide range of geographical regions. Corn is grown in both irrigated and rain-fed areas, with production spanning from the tropical south to the northern plains. The following states are the primary contributors to India’s corn production:
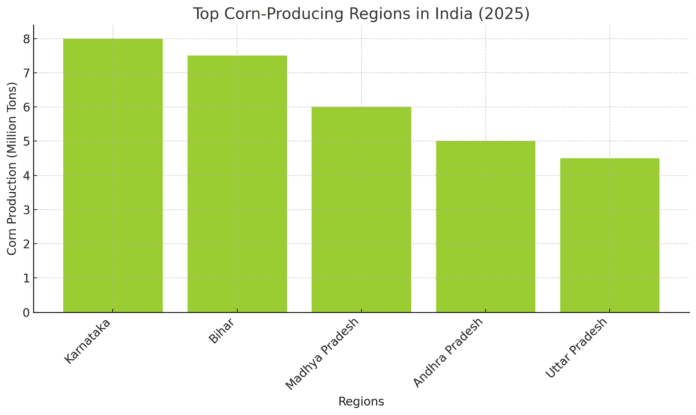
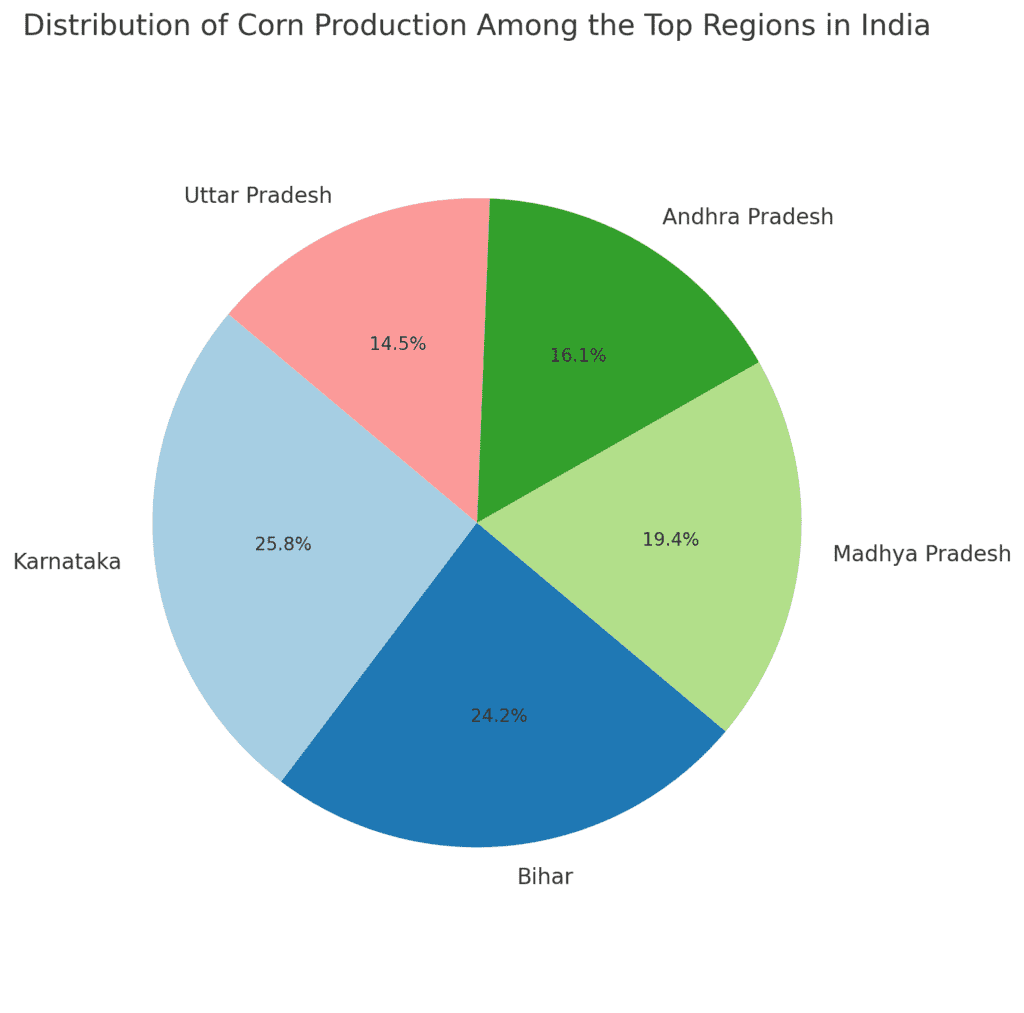
1. Karnataka
Karnataka, located in southern India, is the largest corn-producing state in the country. The state’s favorable climate and fertile soil make it an ideal location for maize farming. Corn is grown in both the rain-fed regions and irrigated lands, with high yields due to the adoption of modern farming techniques. Karnataka’s maize production supports both the domestic market and export opportunities, particularly for animal feed and starch production.
Key facts:
- Largest producer of maize in India
- Key regions: Davanagere, Tumkur, and Bellary
- Key uses: Animal feed, starch production, and exports
2. Bihar
Bihar, in eastern India, is another important producer of corn. The state has seen a steady increase in maize farming, thanks to government policies aimed at supporting the crop. Bihar’s maize is primarily used for food and feed, with a large portion of production going toward the poultry and livestock sectors. The state also benefits from good irrigation infrastructure, further boosting corn yields.
Key facts:
- One of the largest producers of maize in India
- Major regions: Patna, Nalanda, and Begusarai
- Primary uses: Food products, animal feed
3. Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh, located in central India, has witnessed significant growth in maize production over the past few decades. The state has a mix of rain-fed and irrigated lands, which support maize cultivation. Madhya Pradesh’s maize is primarily used in animal feed, with increasing production of maize for biofuels as well.
Key facts:
- Growing corn production in central India
- Key regions: Indore, Ujjain, and Gwalior
- Primary uses: Animal feed, biofuels
4. Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh in the south of India is another key region for maize cultivation. The state’s warm climate and good irrigation facilities have made it an important producer of maize. Andhra Pradesh’s maize production is largely used in the poultry industry and as raw material for corn-based products.
Key facts:
- Significant maize production in southern India
- Major regions: West Godavari, Khammam, and Prakasam
- Main uses: Poultry feed and food products
5. Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous state, also produces a significant amount of corn. While maize is not as dominant as rice or wheat in the state, Uttar Pradesh’s maize is increasingly being used for animal feed and industrial applications. The state’s northern location and its fertile plains contribute to its maize production capacity.
Key facts:
- Growing importance in maize production
- Major regions: Gorakhpur, Deoria, and Varanasi
- Primary uses: Animal feed and food products
Key Companies in India’s Corn Industry
Several companies are involved in India’s corn industry, from farming and processing to trading and export. These companies are crucial in driving the growth of the sector by improving productivity, investing in technology, and securing markets for maize products.
1. Nutrien Ag Solutions India
Nutrien Ag Solutions is one of the leading agribusiness companies involved in the corn sector in India. The company provides a wide range of agricultural solutions, including seeds, fertilizers, and crop protection products, to help farmers improve maize yields. Nutrien is actively involved in the corn farming sector, supporting growers across the country.
Key facts:
- Provides agricultural solutions for maize farmers
- Focus on increasing maize yields through technology
- Key player in the agricultural input sector
2. Cargill India
Cargill is one of the leading global agribusiness companies with a strong presence in India. Cargill’s operations in India are focused on trading, processing, and marketing corn-based products. The company sources corn from Indian farmers and processes it for food and feed applications. Cargill is a significant player in the Indian corn industry, helping to meet both domestic demand and export requirements.
Key facts:
- Focuses on corn-based food and feed products
- Key player in grain trading and processing
- Large network for sourcing and distribution
3. Monsanto India (Bayer CropScience)
Monsanto, now part of Bayer CropScience, is a major player in India’s maize industry, particularly in the seed sector. The company provides high-yielding hybrid maize seeds to Indian farmers, helping them increase productivity and improve crop quality. Monsanto’s investment in research and development has made it a leader in the seed market.
Key facts:
- Provides hybrid maize seeds to Indian farmers
- Focuses on increasing maize yields through genetics
- Research-driven innovation in maize seed production
Challenges Facing India’s Corn Industry
Despite India’s strong position as a maize producer, there are several challenges facing the industry that could affect future growth:
1. Water Scarcity and Irrigation
Many maize-growing regions in India rely heavily on irrigation, and the availability of water can be a limiting factor for maize production. Climate change and irregular rainfall patterns have exacerbated water scarcity in some areas, affecting yields and making maize farming less predictable.
2. Price Volatility
Maize prices in India can fluctuate significantly, affecting both farmers and consumers. While maize is a critical crop for the livestock sector, price instability can make it difficult for farmers to plan and invest in their crops.
3. Land Ownership Issues
In India, many farmers still face challenges related to land ownership, which can limit access to capital, technology, and modern farming methods. The fragmented nature of landholdings in some regions means that many maize farmers operate on small-scale farms, which can reduce efficiency and profitability.
Future Opportunities
The future of India’s corn industry looks promising, with several opportunities for growth:
- Increasing Demand for Animal Feed: As India’s poultry and livestock industries continue to grow, the demand for maize as animal feed is expected to increase. This provides a stable market for maize production in India.
- Biofuels and Industrial Applications: India’s focus on renewable energy and biofuels creates an opportunity for increased maize production for ethanol production.
- Technological Advancements: The use of modern farming techniques, including precision farming and improved irrigation, can help increase maize yields and reduce the impact of climate change.
Conclusion
India’s corn industry plays a vital role in the agricultural economy, with key regions such as Karnataka, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, and Andhra Pradesh driving production. The sector supports food security, animal feed production, and industrial applications, while companies like Nutrien, Cargill, and Bayer CropScience continue to innovate and support farmers. However, challenges such as water scarcity, price volatility, and land ownership remain issues that need addressing. With the right investments in technology, infrastructure, and policies, India’s maize industry has the potential for sustained growth and to play a key role in global corn markets.



