Introduction
Rye has been a staple crop in Russia for centuries, playing an essential role in the country’s agricultural and culinary heritage. With its hardiness and ability to thrive in colder climates, rye is well-suited to the Russian landscape, particularly in the vast expanses of Siberia and the European part of the country. Rye production in Russia is a crucial component of both the domestic food industry and international markets, especially as demand for rye-based products like bread and whiskey continues to grow globally.
🚀 Supercharge Your Insights with ESS Pro
Access over 50,000 expert market reports and connect with more than 500,000 verified industry contacts across the global food & beverage value chain.
Includes exclusive insights, top 10 rankings, live market indicators, and up to 10 custom research reports annually.
🔓 Join ESS Pro – Unlock Full AccessThis report takes an in-depth look at the top rye-producing regions in Russia, focusing on the geographic areas where rye cultivation thrives, the factors influencing production, and how these regions contribute to Russia’s position as the world’s largest producer of rye.
Why is Rye Important in Russia?
Rye (Secale cereale) is a cereal grain closely related to wheat and barley. It has been a central crop in Russia due to its resilience in harsh climates and poor soil conditions. Rye is used primarily for bread-making, with traditional rye bread being a dietary staple in Russian cuisine. Additionally, rye is used in the production of alcohol, including vodka and whiskey, which are important exports for Russia.
Rye is also essential for livestock feed, particularly in the country’s agricultural system, where rye is often used as part of crop rotation systems to improve soil health. Rye’s ability to grow in cold temperatures makes it particularly suited for the northern and eastern regions of Russia, where other crops may not thrive as well.
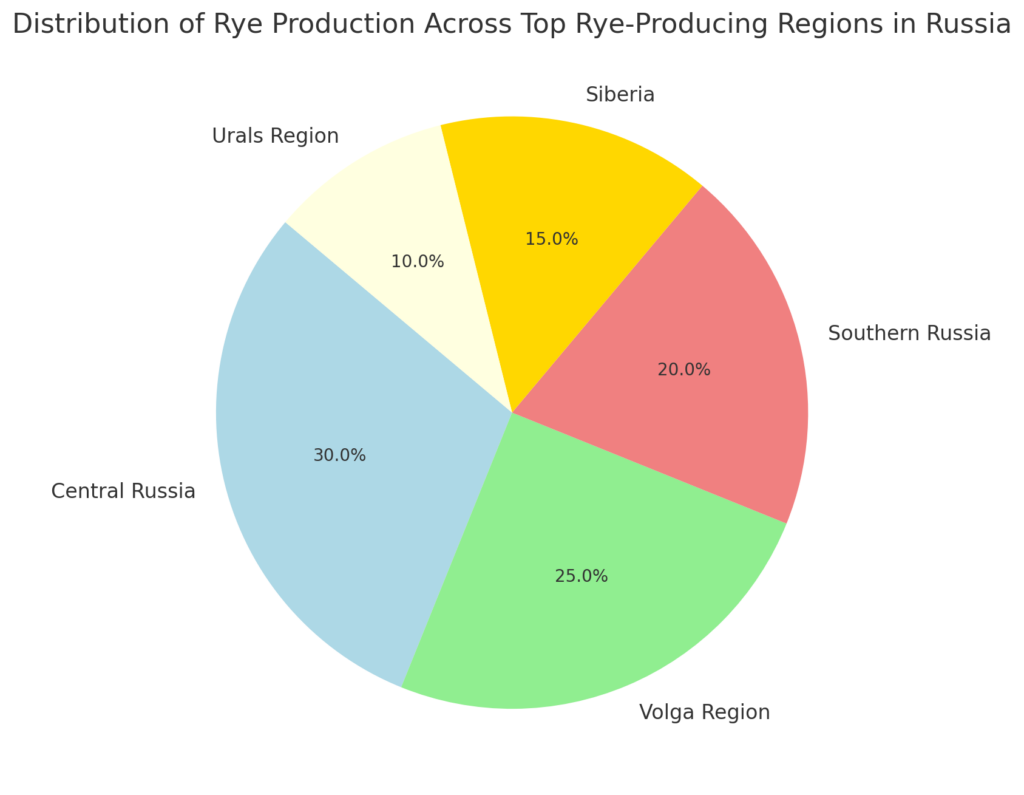
Key Rye-Producing Regions in Russia
1. Central Russia
The Central Russian region is one of the most important areas for rye cultivation in the country. This area includes regions like Moscow, Tula, and Ryazan, which are known for their fertile soil and relatively moderate climate. Central Russia benefits from a combination of well-established farming infrastructure and favorable growing conditions for rye, making it one of the largest rye-producing areas in the country.
Rye in Central Russia is primarily grown for the domestic market, where it is used in the production of rye bread and other baked goods. The region’s proximity to major urban centers, including Moscow, allows for efficient distribution of rye-based products to the population. The demand for rye in this area is driven by both traditional Russian culinary preferences and the growth of the bread and snack industries.
2. Volga Region
The Volga region, stretching from the western part of Russia along the Volga River, is another key area for rye production. This region includes areas like Samara, Saratov, and Volgograd, which have a long history of grain production. The Volga region is particularly known for its dryland farming, with rye being a major crop alongside wheat and barley.
The Volga region’s climate is more arid compared to other parts of Russia, but rye’s hardiness makes it a viable crop for this area. Rye is grown for both food production and as a feed crop for livestock. Additionally, the Volga region is home to several large agricultural companies that specialize in grain production and processing, further cementing its role in Russia’s rye industry.
The proximity of the Volga region to both domestic and international markets also makes it an essential area for exporting rye-based products. The region’s location along major transportation routes, including the Volga River and railway lines, facilitates the movement of rye to other parts of Russia and beyond.
3. Southern Russia
Southern Russia, including regions such as Krasnodar, Rostov, and Stavropol, is one of the warmest areas for rye production in the country. The climate here is more temperate, with longer growing seasons that are ideal for crops like rye, wheat, and corn. Rye in the southern regions is often grown as part of crop rotation systems to maintain soil health and reduce pest pressure.
The Southern Russia region is a major agricultural hub for the country, and rye plays a significant role in the local economy. Rye from this region is often used for bread-making and is known for its high-quality grains. The Southern Russia region also has a strong export market, with rye products being sent to countries in Europe and Asia.
In addition to rye, the Southern Russia region is a key area for producing other grains, such as wheat and barley, which are important for both domestic consumption and export. The region’s infrastructure, including large ports on the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov, allows for efficient export of rye and other agricultural products.
4. Siberia
Siberia, one of the largest and most remote regions of Russia, is an important area for rye cultivation. Despite the cold temperatures and harsh growing conditions, Siberia’s expansive land area provides the space needed for large-scale grain production. Regions like Altai, Omsk, and Novosibirsk are major contributors to Russia’s overall rye production.
The climate in Siberia can be challenging for crop production, but rye’s ability to tolerate cold and poor soil conditions makes it a viable option for farmers in the region. Rye is typically grown in the more southern parts of Siberia, where the climate is slightly milder, and the growing season is longer. In these areas, rye is used for bread-making and as a feed crop for livestock.
Siberia’s rye production is essential for the domestic market, particularly in rural areas where rye-based products like bread are a dietary staple. Additionally, the vast size of the region and its remote location make it important for food security, ensuring that rye is grown even in the more isolated parts of Russia.
5. Urals Region
The Urals region, located to the east of the Volga region, is another important area for rye production in Russia. This region includes Sverdlovsk, Chelyabinsk, and Kurgan, which are known for their diverse agricultural activities. Rye is grown in the Urals for both food and animal feed, and it is an essential crop in the area’s crop rotation systems.
The Urals region experiences a harsher climate compared to areas further south, but rye’s hardiness makes it a suitable crop for the region. The area’s agriculture is characterized by a mix of large-scale commercial farming and small, family-owned farms, both of which contribute to the region’s rye production.
The Urals’ location between Europe and Asia also makes it an important center for trade, and rye from the region is distributed both domestically and internationally.
Factors Driving Rye Production in Russia
Several factors contribute to the success of rye production in Russia’s top rye-producing regions. These factors include:
- Climate Conditions: Rye thrives in colder climates with shorter growing seasons, making it ideal for Russia’s diverse climates, from the cold northern regions to the milder southern areas.
- Soil Quality: Rye is known for its ability to grow in poor soil conditions, which makes it suitable for regions with less fertile land, such as parts of Siberia and the Volga region.
- Cultural Significance: Rye has deep cultural ties to Russian cuisine, particularly in the form of traditional rye bread. This cultural demand for rye products helps support its cultivation in key regions.
- Economic Importance: Rye production is a vital part of Russia’s agricultural economy, providing food, feed, and raw materials for the spirits industry. As demand for rye-based products grows, especially in the export market, rye cultivation continues to thrive.
- Government Support: Russian agricultural policies often support grain production, including rye, through subsidies, price controls, and other incentives. This support helps farmers in key regions maintain profitability and production levels.
Conclusion
Russia is the world’s largest producer of rye, and its top rye-producing regions play a critical role in meeting both domestic demand and global supply. The regions of Central Russia, the Volga, Southern Russia, Siberia, and the Urals are central to the country’s rye industry, with favorable growing conditions and strong infrastructure supporting the growth and distribution of rye. As global demand for rye-based products continues to rise, these regions will remain at the forefront of the rye market, contributing to Russia’s dominant position in global rye production.



