Bananas are one of the most widely grown and consumed fruits in India. Known for their versatility, taste, and nutritional value, bananas are a staple in Indian households and are an integral part of the country’s agricultural landscape. India is not only the largest banana producer in the world but also home to a variety of bananas that cater to diverse tastes and preferences.
In this article, we explore the top 10 banana-producing states in India, their production levels, and their contribution to the economy and agriculture.

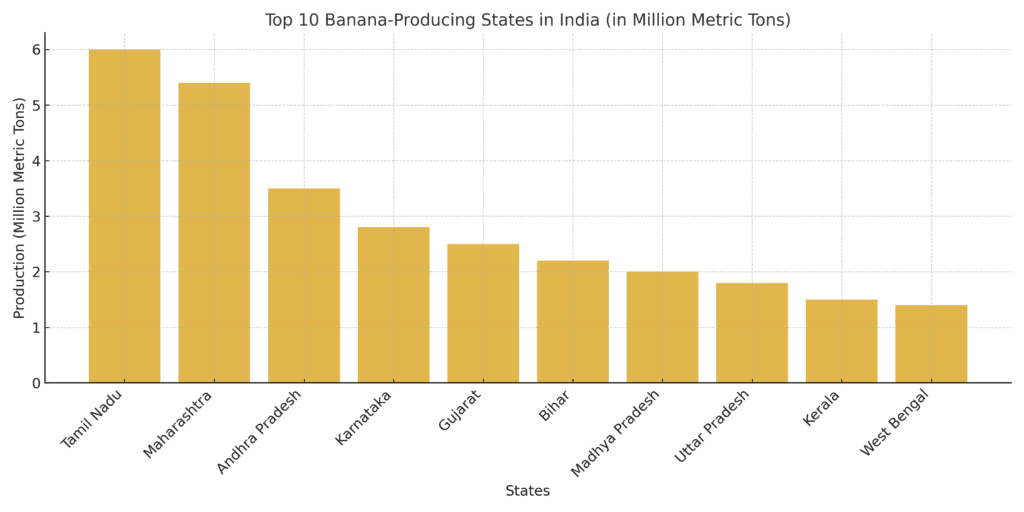
1. Tamil Nadu
The Banana Powerhouse of India
Production: Over 6 million metric tons annually
Tamil Nadu leads banana production in India, contributing nearly 20% of the country’s output. The state’s favorable climate and fertile soil, particularly in districts like Tiruchirappalli, Coimbatore, and Erode, make it ideal for banana farming. Popular varieties include Robusta, Nendran, and Poovan. Tamil Nadu is also known for its innovative farming techniques and high-yield plantations.
2. Maharashtra
A Rising Star in Banana Production
Production: Approximately 5.4 million metric tons annually
Maharashtra is a close competitor to Tamil Nadu, with its production concentrated in regions like Jalgaon, also known as the “Banana City of India.” Farmers in Maharashtra primarily grow Cavendish bananas, which are highly sought after for both domestic consumption and exports. The state has embraced drip irrigation and other modern techniques, boosting yields significantly.
3. Andhra Pradesh
A Hub for High-Quality Bananas
Production: Around 3.5 million metric tons annually
Andhra Pradesh has emerged as a significant banana producer, with areas like Kadapa and Guntur leading the charge. The state focuses on growing robust varieties like Grand Naine and Tella Chakkerakeli. Andhra Pradesh’s bananas are known for their superior taste and quality, making them popular in markets across India.
4. Karnataka
Balancing Quantity and Quality
Production: Approximately 2.8 million metric tons annually
Karnataka’s banana production is concentrated in districts such as Mysuru, Chikkamagaluru, and Belagavi. The state grows diverse varieties, including Rasabale and Elakki, which are often used in traditional dishes and desserts. Karnataka has also adopted sustainable farming practices to improve productivity and environmental impact.
5. Gujarat
Thriving with Advanced Techniques
Production: Around 2.5 million metric tons annually
Gujarat has made remarkable progress in banana production, particularly in districts like Bharuch and Vadodara. The state’s farmers have adopted tissue culture methods and precision farming, enabling higher yields. Gujarat primarily grows Cavendish bananas, which are consumed locally and exported to other states.
6. Bihar
A Traditional Banana Giant
Production: Approximately 2.2 million metric tons annually
Bihar is one of the oldest banana-producing regions in India. The state’s fertile Gangetic plains, particularly in districts like Vaishali and Muzaffarpur, provide ideal conditions for banana cultivation. Farmers here focus on varieties like Malbhog and G9. Bananas are a vital part of the state’s agricultural economy, providing livelihoods for thousands of farmers.
7. Madhya Pradesh
A Rapidly Growing Contender
Production: Around 2 million metric tons annually
Madhya Pradesh has witnessed significant growth in banana farming over the past decade. Districts like Burhanpur and Khandwa are emerging as key production centers. The state primarily grows Grand Naine bananas, leveraging modern irrigation systems and government support to boost production.
8. Uttar Pradesh
Sustaining Tradition and Modernity
Production: Approximately 1.8 million metric tons annually
Uttar Pradesh is another prominent banana-producing state, with its production concentrated in regions like Kushinagar and Gorakhpur. Farmers in the state cultivate popular varieties like G9 and Dwarf Cavendish. Uttar Pradesh’s bananas are consumed locally and also sent to neighboring states.
9. Kerala
Specialty Bananas for Niche Markets
Production: Around 1.5 million metric tons annually
Kerala is renowned for its unique banana varieties, such as Nendran and Palayamkodan. These bananas are widely used in traditional dishes like banana chips and payasam. Kerala’s banana farming is concentrated in regions like Thrissur and Palakkad, where the tropical climate supports year-round cultivation.
10. West Bengal
A Blend of Tradition and Innovation
Production: Approximately 1.4 million metric tons annually
West Bengal contributes significantly to India’s banana production, with districts like Nadia and Murshidabad leading the way. The state primarily grows varieties like Mortman and Champa, which are well-loved for their taste and texture. Banana farming in West Bengal supports small-scale farmers and plays a vital role in rural livelihoods.
The Economic Importance of Bananas in India
Bananas are not just a popular fruit in India; they are an economic lifeline for millions. Here’s why bananas are vital to India’s economy:
- Employment: Banana farming provides direct and indirect employment to millions of farmers, traders, and workers in the supply chain.
- Domestic Consumption: With over 95% of bananas consumed within the country, they are a staple in Indian diets and an affordable source of nutrition.
- Exports: Though a smaller portion, Indian bananas are exported to the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and Europe, earning valuable foreign exchange.
- Value-Added Products: Bananas are processed into products like chips, purees, and powders, creating additional revenue streams.
Challenges in the Indian Banana Industry
Despite its impressive production, the banana industry in India faces several challenges:
- Pests and Diseases: Fungal diseases like Panama disease and pests like banana weevils threaten yields.
- Climate Change: Erratic weather patterns and water scarcity affect banana cultivation.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Poor storage and transportation facilities lead to post-harvest losses.
- Market Fluctuations: Farmers often struggle with price volatility and lack of access to stable markets.
The Future of Banana Production in India
To sustain its leadership in banana production, India must focus on the following:
- Adopting Technology: Precision farming, tissue culture, and drip irrigation can improve yields and quality.
- Infrastructure Development: Building better storage, transportation, and marketing facilities can reduce losses and improve profitability.
- Sustainability Practices: Encouraging organic farming and reducing pesticide use will ensure long-term environmental health.
- Market Access: Expanding export markets and establishing fair trade practices can benefit farmers.
Conclusion
India’s banana production is a testament to the country’s agricultural prowess. From Tamil Nadu’s vast plantations to Kerala’s unique specialty bananas, each state contributes uniquely to the nation’s banana basket. By embracing modern techniques and addressing challenges, India can continue to dominate global banana production and improve the livelihoods of millions involved in the industry.
Bananas are not just a fruit—they are a symbol of resilience, diversity, and sustainability in Indian agriculture. As the demand for this versatile fruit continues to grow, India’s banana industry is poised to reach new heights.