Introduction
The global meat industry remains a cornerstone of the world’s food supply, with billions of people relying on meat as a primary source of protein. In 2025, the industry faces both unprecedented challenges and exciting opportunities. Factors such as shifting consumer preferences, technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and geopolitical influences are reshaping how meat is produced, processed, distributed, and consumed worldwide. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of the current state of the global meat industry, highlighting key trends, challenges, and future outlook.
🚀 Supercharge Your Insights with ESS Pro
Access over 50,000 expert market reports and connect with more than 500,000 verified industry contacts across the global food & beverage value chain.
Includes exclusive insights, top 10 rankings, live market indicators, and up to 10 custom research reports annually.
🔓 Join ESS Pro – Unlock Full Access
1. Global Meat Production Trends
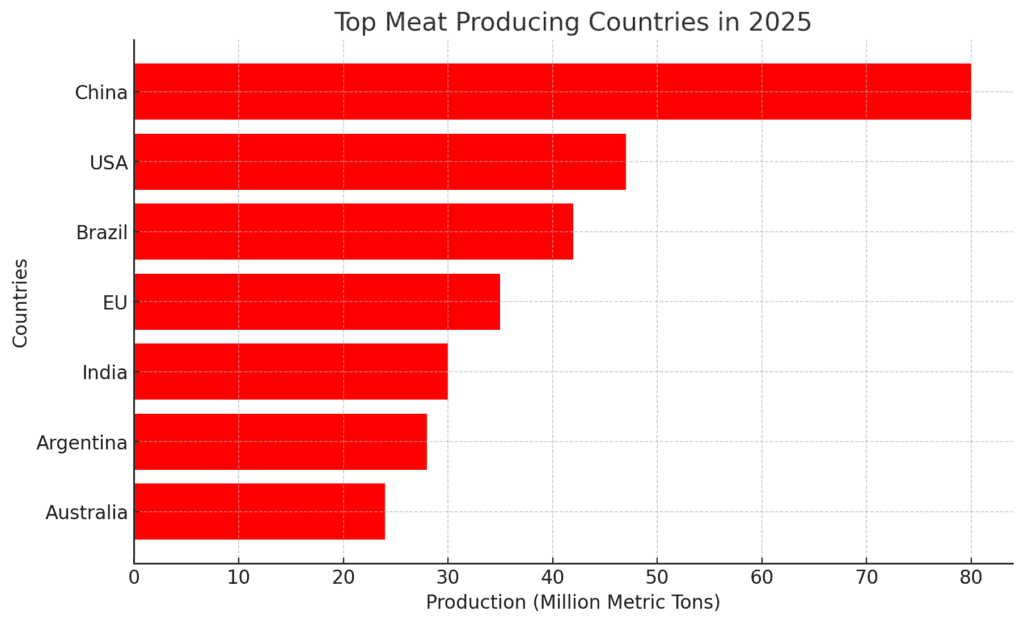
1.1 Leading Meat-Producing Countries
The global meat production landscape is dominated by a few key players:
- China remains the world’s largest producer of pork, with continued investment in biosecure pig farms.
- Brazil leads in beef and poultry exports, with new trade deals expanding market access.
- United States maintains its position as a top producer of beef, poultry, and pork.
- India is a dominant player in buffalo meat exports, catering to Middle Eastern and Asian markets.
- European Union remains a major producer, though stricter sustainability laws are reshaping livestock farming practices.
1.2 Growth in Alternative Production Regions
New players in Africa and Southeast Asia are increasing their meat production capacity, supported by foreign investments in agriculture and livestock farming. Countries like Vietnam, Nigeria, and Ethiopia are emerging as regional meat suppliers.
2. Global Meat Trade and Market Dynamics
2.1 Top Exporters and Importers
- Brazil, the U.S., and Australia remain the largest meat exporters, supplying beef, pork, and poultry to global markets.
- China, Japan, and South Korea lead in meat imports due to high domestic demand and reliance on foreign supply chains.
- The European Union continues to import high-quality beef from South America while exporting pork to Asia.
2.2 Key Trade Agreements and Tariff Changes
New trade deals, including revised EU-Mercosur agreements and U.S.-China meat trade agreements, are shaping the flow of global meat exports. Stricter sustainability and animal welfare regulations are also influencing market access.
3. Consumer Trends and Preferences in 2025
3.1 Demand for Sustainable Meat
Consumers in North America and Europe are increasingly demanding sustainably sourced meat, leading companies to invest in carbon-neutral and regenerative livestock farming practices.
3.2 Rise of Premium and Specialty Meats
- Grass-fed and organic meats are gaining popularity among health-conscious consumers.
- Halal and kosher-certified meats continue to see strong demand in the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
- Wagyu and dry-aged beef are experiencing growth in premium dining markets.
3.3 Shift Toward Alternative Proteins
While traditional meat remains dominant, lab-grown meat, plant-based proteins, and hybrid meat-plant products are capturing market share, particularly among younger consumers.
4. Challenges Facing the Meat Industry
4.1 Climate Change and Environmental Concerns
Livestock farming remains under scrutiny for its carbon footprint, deforestation impact, and high water usage. Governments are enforcing stricter emissions regulations, while meat producers are investing in methane-reducing feed technologies and improved waste management.
4.2 Supply Chain Disruptions
Ongoing global logistics challenges, including port congestion, feed shortages, and disease outbreaks such as African Swine Fever (ASF) and Avian Influenza, continue to disrupt meat supply chains.
4.3 Rising Production Costs
Inflationary pressures are pushing up the costs of feed, labor, and transportation. Many companies are passing these costs onto consumers, affecting affordability and demand.
5. Technological Innovations in the Meat Industry
5.1 Precision Livestock Farming
Smart farming techniques, such as IoT-enabled sensors, AI-driven animal health monitoring, and automated feeding systems, are improving efficiency and animal welfare.
5.2 Blockchain for Meat Traceability
Blockchain technology is gaining traction in ensuring transparency and traceability in meat production, helping retailers verify sourcing claims and combat food fraud.
5.3 AI and Robotics in Meat Processing
Meatpacking plants are increasingly adopting robotics and AI-powered quality control systems to improve efficiency, safety, and hygiene in meat processing facilities.
6. Regional Market Insights
6.1 North America
The U.S. and Canada are experiencing steady growth in premium meat segments and exports to Asia. However, labor shortages in meat processing remain a challenge.
6.2 South America
Brazil and Argentina are expanding their beef export capabilities while dealing with deforestation-related criticisms.
6.3 Europe
Stricter environmental and animal welfare regulations are driving changes in meat production practices. Consumer preferences are shifting toward organic and ethically produced meat.
6.4 Asia-Pacific
China remains the world’s largest pork consumer, while Japan and South Korea continue to import high-quality beef and seafood.
6.5 Middle East & Africa
Growing urbanization and middle-class expansion are driving meat consumption in regions like the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa.
7. Future Outlook and Growth Opportunities
7.1 Expansion of Sustainable Meat Production
The industry is moving toward carbon-neutral meat production, with major companies investing in eco-friendly practices to meet consumer and regulatory demands.
7.2 Growth in Online Meat Retail and Subscription Services
E-commerce platforms and direct-to-consumer meat subscription services are growing, with consumers valuing convenience and transparency.
7.3 Increased Investment in Alternative Meat Proteins
While traditional meat remains dominant, alternative proteins are expected to take a larger market share, prompting meat companies to diversify their product offerings.
7.4 Development of High-Tech Meat Processing Facilities
Automated meat processing plants with AI-driven quality control systems will become the industry norm, improving efficiency and food safety.
8. SEO & Digital Marketing Strategies for Meat Companies
8.1 Keyword Optimization for Search Engines
Popular SEO keywords for the meat industry include:
- “Global meat market trends 2025”
- “Sustainable meat production practices”
- “Top meat exporting countries”
- “Best premium beef brands”
- “Meat industry challenges and opportunities”
8.2 Content Marketing for Meat Producers
- Regular industry reports and blog posts on sustainability, market trends, and new product launches.
- Social media campaigns highlighting ethical farming practices.
- Educational content on meat nutrition and cooking tips.
8.3 Video Marketing & Influencer Collaborations
YouTube and TikTok marketing strategies featuring farm-to-table videos, chef collaborations, and meat processing insights can enhance brand engagement.
Conclusion
The global meat industry in 2025 is undergoing a transformative phase driven by technological advancements, sustainability pressures, and shifting consumer demands. While traditional meat consumption remains strong, the rise of alternative proteins, precision farming, and AI-driven processing is reshaping the future of meat production. Companies that prioritize sustainability, digital transformation, and consumer engagement will be best positioned for long-term success in the evolving global meat market.