Introduction
Watermelons are among the most widely consumed fruits globally, with demand driven by their refreshing taste, high water content, and nutritional benefits. The watermelon industry is a vital component of the global agricultural economy, with production concentrated in key regions such as China, India, the United States, and Brazil. In 2025, the industry continues to evolve with advancements in farming techniques, shifting consumer preferences, and trade dynamics impacting production, distribution, and pricing.
Market Overview
The global watermelon market is projected to exceed $50 billion by 2025, fueled by increasing health consciousness among consumers, rising demand for natural hydration solutions, and innovations in seedless and mini watermelons. Major exporters include China, Turkey, and Spain, while the U.S., Germany, and Japan are among the top importers. The industry has also witnessed the emergence of large-scale commercial farming projects to cater to expanding markets in the Middle East and Africa.
Leading Producing Countries
- China – The world’s largest watermelon producer, accounting for over 60% of global supply.
- India – A significant producer, with domestic consumption driving demand.
- Brazil – Leading South American producer, with increasing exports to North America.
- Turkey – Major supplier to European and Middle Eastern markets.
- United States – Production concentrated in Texas, California, and Florida, with a focus on hybrid varieties.
Key Trends in the Watermelon Industry
- Sustainability & Water Efficiency: Watermelon farming is water-intensive, leading to increased adoption of smart irrigation systems and drought-resistant varieties.
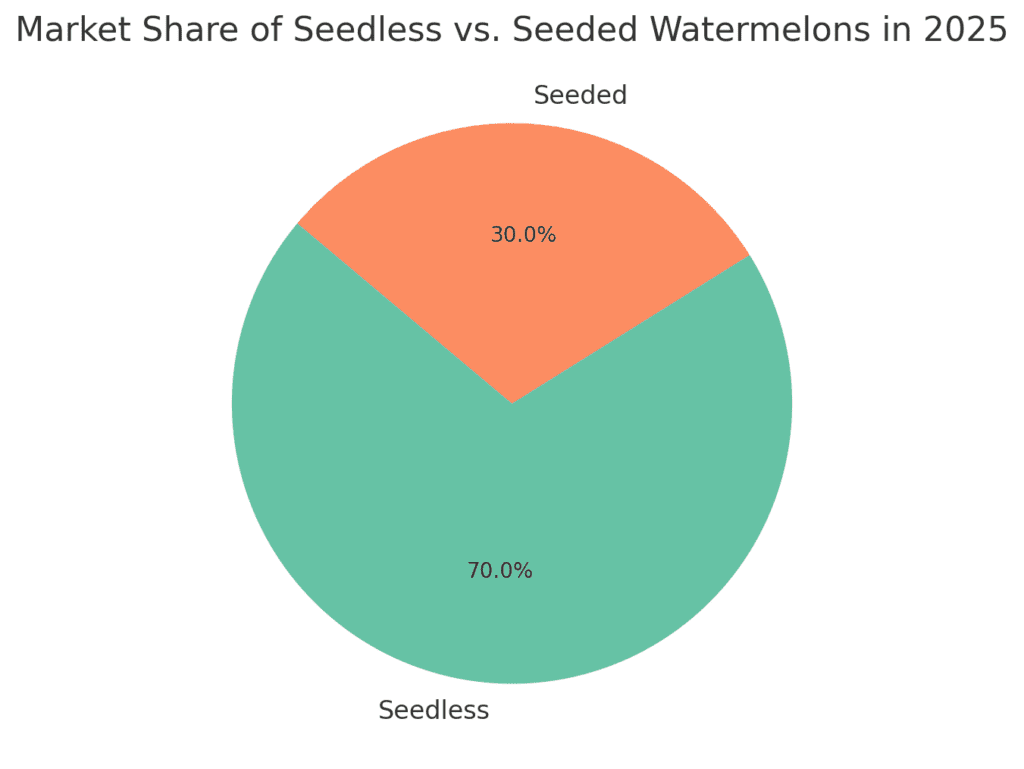
- Growing Demand for Seedless Watermelons: Consumers prefer convenience, leading to rising market share for seedless varieties.
- Organic & Non-GMO Production: The market for organic watermelons is expanding, particularly in North America and Europe.
- Innovations in Packaging & Logistics: Companies are investing in biodegradable packaging and cold chain logistics to reduce waste and improve export quality.
- Health-Driven Consumption: Watermelons are rich in antioxidants, making them popular among health-conscious consumers.
Major Companies in Watermelon Production & Distribution
- Syngenta – A global leader in watermelon seed genetics, driving hybrid variety development.
- Monsanto (Bayer CropScience) – Innovating in seed technology to improve disease resistance and yield.
- Fresh Del Monte – One of the largest distributors of fresh watermelons worldwide.
- Dole Food Company – Focuses on large-scale farming and retail partnerships.
- NatureSweet – A leader in greenhouse-grown watermelons, ensuring year-round supply.
- Agrícola Famosa – Brazil’s top watermelon producer and key exporter to Europe.
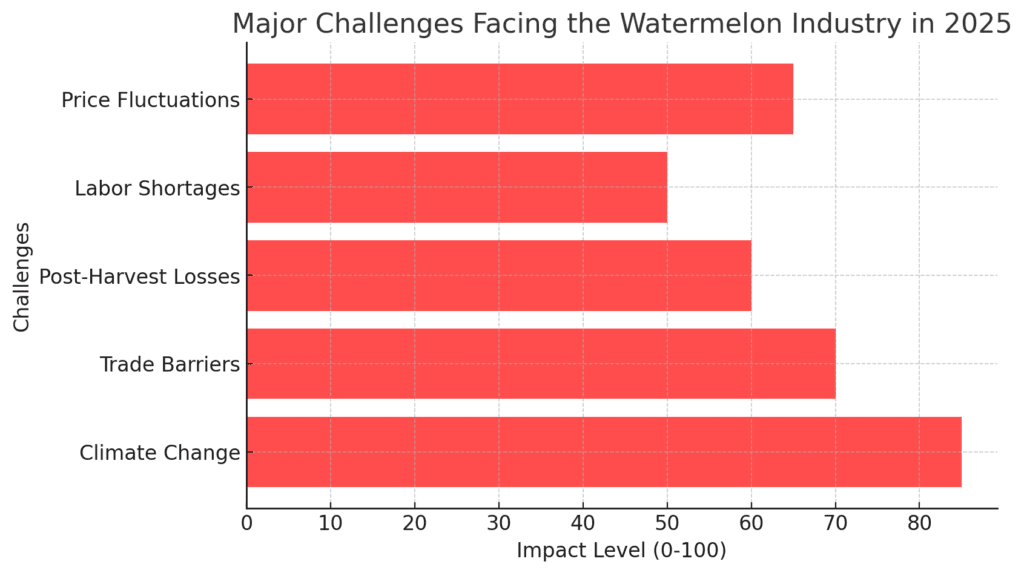
Challenges Facing the Watermelon Industry
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather patterns affecting yields and water availability.
- Trade Barriers & Tariffs: Exporters face tariffs and phytosanitary restrictions in key markets.
- Post-Harvest Losses: A significant percentage of watermelons are wasted due to perishability and inefficient logistics.
- Labor Shortages: Mechanization in watermelon harvesting remains limited, leading to labor dependency.
- Price Fluctuations: Seasonal production cycles cause price volatility in global markets.
Innovations & Future Prospects
- AI & Precision Farming: Drones and satellite imagery are being used to monitor crop health and optimize yields.
- Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: Companies are adopting blockchain technology for traceability in the watermelon trade.
- Expansion of Hydroponic Watermelon Farming: Hydroponic techniques are being explored for sustainable production in urban areas.
- Vertical Integration: More companies are investing in farm-to-table models, reducing intermediaries.
- Functional Watermelon Products: Growth in watermelon-based beverages, snacks, and dietary supplements is expanding market opportunities.
Conclusion
The watermelon industry in 2025 is characterized by strong growth, sustainability initiatives, and technological advancements. While challenges such as climate change and trade barriers persist, innovations in farming, logistics, and branding continue to drive the sector forward. As global demand increases, industry players must focus on efficient supply chain management, consumer trends, and regulatory compliance to stay competitive in the evolving market landscape.