
Introduction
Indonesia, an archipelago of over 17,000 islands, is one of Southeast Asia’s largest agricultural producers. Corn (also known as maize) is an essential crop in Indonesia, playing a vital role in food security, animal feed, and industrial applications. Although rice remains the primary staple food in Indonesia, corn is increasingly being used in a variety of products, including food for humans, livestock feed, and biofuels. In this report, we explore Indonesia’s corn production industry, examining the largest producing regions, key companies, and the factors influencing the sector’s growth.
Corn Production in Indonesia
Indonesia’s maize industry has seen significant growth in recent years, driven by rising demand for corn in food products, animal feed, and industrial uses. Corn is grown throughout the country, but certain regions are better suited for its cultivation due to favorable soil and climatic conditions. Maize is grown in both large-scale commercial farms and smaller, family-operated farms, with different varieties being produced for various purposes.
Indonesia is a net importer of corn, relying on imports to meet the demand for its rapidly growing livestock industry and food processing sector. However, the country has made strides toward increasing its domestic corn production to reduce reliance on imports. According to the Indonesian Ministry of Agriculture, maize production in Indonesia has steadily increased over the past decade, with output reaching around 25 million tons in recent years.
Key Corn-Producing Regions in Indonesia
The success of Indonesia’s corn industry is largely attributed to several key regions where maize cultivation thrives. These regions benefit from fertile soil, favorable rainfall patterns, and advanced farming techniques that ensure high productivity.
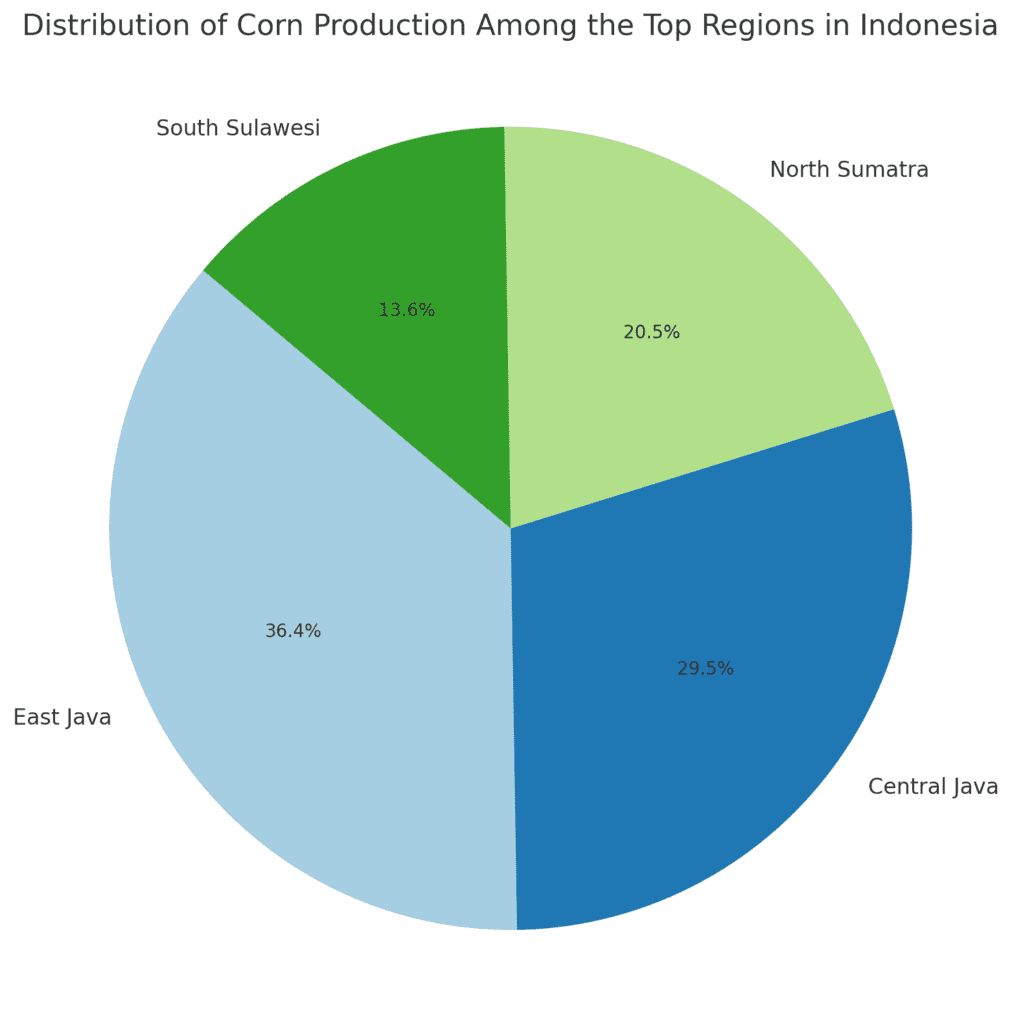
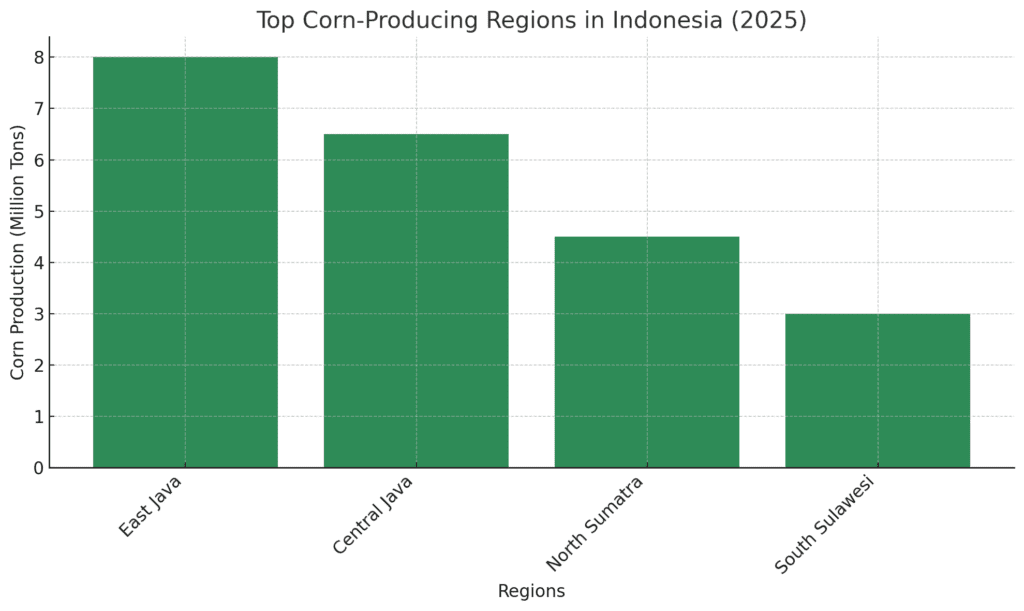
1. East Java
East Java is the largest corn-producing province in Indonesia, contributing a significant portion of the country’s overall corn production. The region’s favorable climate and large agricultural land areas make it an ideal location for corn farming. East Java’s corn production is mainly focused on supplying local markets, although some maize is also processed for animal feed and export.
East Java is also home to numerous maize processing plants that turn harvested corn into products like corn flour, cornmeal, and livestock feed. The province’s central location within the country’s transportation network makes it a hub for the distribution of maize to both domestic and international markets.
2. Central Java
Central Java is another major corn-producing region, thanks to its abundant agricultural land and reliable rainfall. The province’s agricultural sector is highly diversified, with corn being a key crop alongside rice, soybeans, and vegetables. Corn is primarily grown in the districts of Magelang, Temanggung, and Klaten, where smallholder farmers use a mix of traditional and modern farming techniques.
The government of Central Java has been active in promoting maize production through initiatives that provide farmers with access to high-quality seeds, fertilizers, and training programs. These efforts have helped improve yields and make the region more competitive in the national and international maize markets.
3. North Sumatra
North Sumatra is another significant maize-producing region in Indonesia. The province’s fertile volcanic soil and tropical climate provide optimal conditions for corn farming. Maize is primarily grown for local consumption, with some production directed toward the growing animal feed sector in Indonesia.
Farmers in North Sumatra face challenges such as limited access to modern farming equipment and market volatility, but the region’s importance in maize production cannot be overstated. Government and private sector efforts to improve the productivity of smallholder farmers are helping North Sumatra maintain its position as a key contributor to Indonesia’s corn industry.
4. South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi, located on the island of Sulawesi, is another important corn-producing region in Indonesia. The province has seen a rise in maize farming due to the growing demand for corn in the livestock industry. Corn is widely grown in the regions of Maros, Pangkep, and Barru, where the local climate is well-suited for maize cultivation.
The province has benefitted from government subsidies for corn production, as well as technical assistance to increase the productivity of local farmers. As a result, South Sulawesi is emerging as a key player in Indonesia’s expanding corn industry.
Key Corn-Producing Companies in Indonesia
Several large agricultural companies in Indonesia are involved in corn farming, processing, and trading. These companies are helping to shape the country’s corn industry by improving farming practices, investing in processing facilities, and expanding their market reach.
1. PT. Bisi International Tbk
PT. Bisi International Tbk is one of Indonesia’s leading agribusiness companies, specializing in the production and distribution of hybrid corn seeds. The company is a key player in Indonesia’s maize industry, supplying high-quality seeds to local farmers and helping them increase their corn yields. Bisi International is also involved in the production of animal feed, which relies heavily on corn as a primary ingredient.
Bisi International’s commitment to research and development ensures that the company remains at the forefront of agricultural innovation in Indonesia. Their high-yielding corn varieties have become popular among Indonesian farmers, leading to increased domestic production.
2. PT. Indofood CBP Sukses Makmur Tbk
Indofood, one of Indonesia’s largest food companies, is a major player in the corn sector, particularly in processing corn into food products. Indofood is involved in producing corn-based snacks, corn flour, and instant noodles, making corn a critical component of their product line. The company also sources corn from local farms to support its food manufacturing operations.
Indofood’s scale and reach within the Indonesian food market have made it a key player in shaping the country’s corn demand. The company continues to support the growth of the local corn industry by investing in sustainable farming and maize processing.
3. PT. Sierad Produce Tbk
PT. Sierad Produce Tbk is one of Indonesia’s largest poultry and animal feed producers, heavily reliant on maize for its feed production. The company has expanded its operations to include large-scale corn farming to secure a steady supply of maize for its production needs. Sierad Produce’s integrated business model, which includes farming, processing, and distribution, has made it a significant contributor to Indonesia’s corn industry.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the growth in maize production, Indonesia’s corn industry faces several challenges. One major issue is the reliance on smallholder farmers, many of whom lack access to modern farming equipment and techniques. Additionally, climate change and inconsistent rainfall patterns in some regions have affected crop yields, leading to fluctuating production levels.
However, there are also significant opportunities for growth in Indonesia’s maize industry. The country’s growing livestock sector creates a rising demand for maize as animal feed, while the expanding food processing industry presents new opportunities for maize-based products. Increased government support and technological advancements in farming practices could further boost production and help meet the demand for maize in both domestic and international markets.
Conclusion
Indonesia’s maize production industry is vital to the country’s agricultural economy, supporting both domestic consumption and the growing animal feed sector. Key regions like East Java, Central Java, and North Sumatra contribute significantly to the country’s corn output, while major companies like PT. Bisi International and Indofood continue to drive innovation and market growth. Despite challenges, Indonesia’s corn industry holds promising potential, with ongoing investments in farming technology and processing facilities expected to improve yields and secure the country’s position as a key player in the global maize market.


