
The Origins of Nestlé: From Infant Formula to Global Powerhouse
Nestlé’s story began in 1866, when Henri Nestlé, a Swiss pharmacist, developed an infant cereal formula that revolutionized child nutrition. His breakthrough product, Farine Lactée, became a lifesaving alternative to breast milk for infants who couldn’t be nursed.
By 1905, Nestlé had merged with the Anglo-Swiss Condensed Milk Company, expanding its dairy product line. This early merger strategy set the foundation for Nestlé’s aggressive global expansion, which continues today.
Key Takeaway:
- Innovation + Mergers fueled Nestlé’s early success.
- The focus on nutrition-based products allowed it to gain trust in multiple markets.
Nestlé’s Expansion into Beverages, Dairy, and Confectionery
Nestlé’s growth accelerated in the 20th century with strategic product diversification:
✅ 1910s-1920s: Entered the chocolate business with the acquisition of brands like Peter’s Chocolate.
✅ 1938: Launched Nescafé, an instant coffee brand that became a worldwide phenomenon.
✅ 1947: Acquired Maggi, a leader in seasonings and soups, expanding into savory foods.
By expanding into coffee, dairy, and confectionery, Nestlé diversified its revenue streams, ensuring its market leadership.
Key Takeaway:
- Nestlé invested in diverse food categories to create a balanced portfolio.
- Brand acquisitions helped it dominate markets beyond dairy.

The Power of Acquisitions: How Nestlé Became an Empire
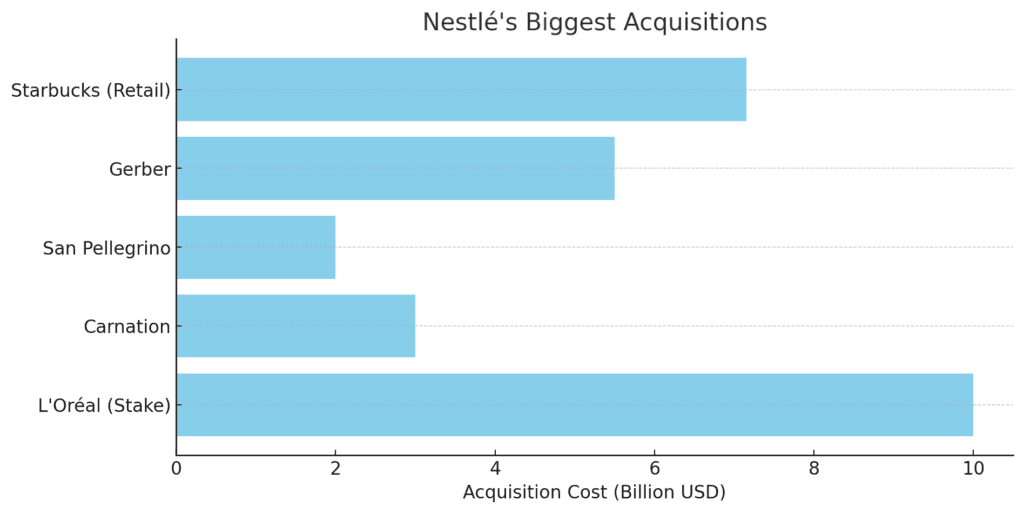
Nestlé has built its dominance through acquisitions, acquiring over 2,000 brands across the food and beverage industry. Some of its biggest and most strategic purchases include:
📌 1974: Became a major stakeholder in L’Oréal, expanding into health and wellness.
📌 1985: Acquired Carnation, adding Evaporated Milk and Coffee-Mate to its lineup.
📌 1998: Bought San Pellegrino, securing a dominant position in premium bottled water.
📌 2007: Acquired Gerber, becoming the leader in infant nutrition.
📌 2018: Bought Starbucks’ retail coffee business for $7.15 billion, strengthening its coffee empire.
These acquisitions gave Nestlé control over key food & beverage categories, ensuring that no competitor could challenge its dominance easily.
Key Takeaway:
- Acquisitions are the backbone of Nestlé’s growth.
- Nestlé eliminates competition by buying strong brands and expanding its portfolio.
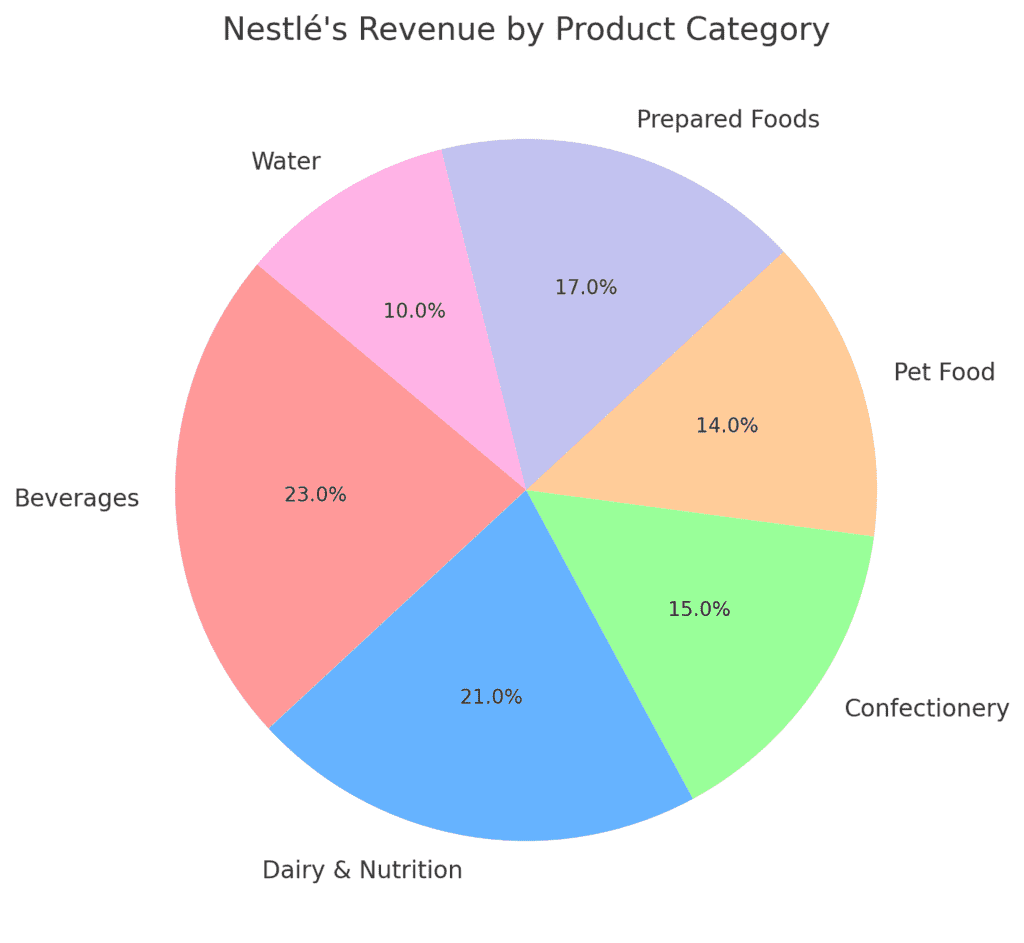
Nestlé’s Global Reach: How It Became the World’s Largest Food Company
Nestlé operates in 188 countries, with over 275,000 employees and more than 400 factories worldwide.
🌎 Presence in Every Market:
- In North America, Nestlé dominates coffee, dairy, and pet food.
- In Europe, it leads in chocolate, bottled water, and baby nutrition.
- In Asia, it has expanded heavily into instant noodles and local flavors.
💰 Financial Strength:
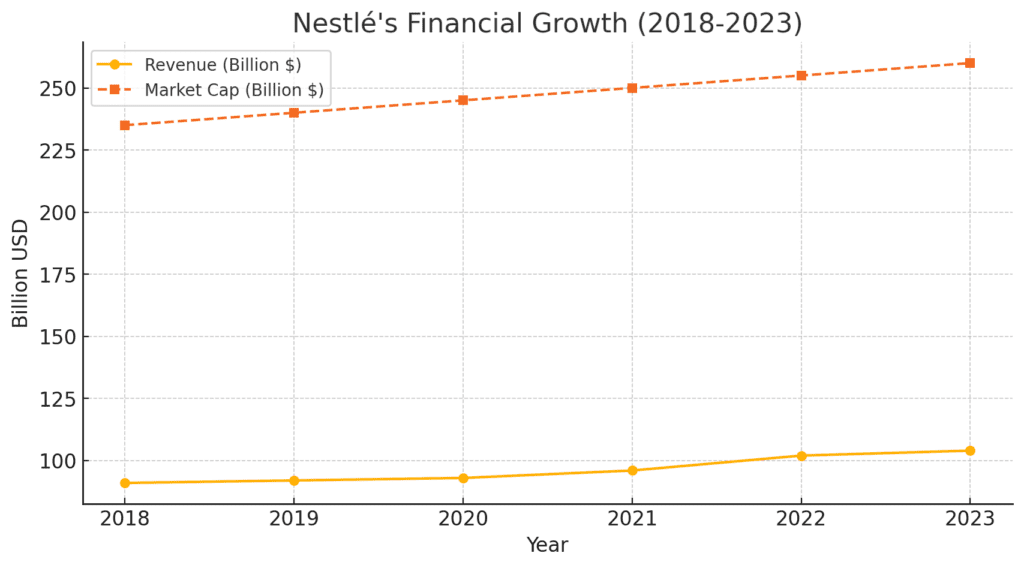
- Annual revenue: $104 billion (2023)
- Market capitalization: $260+ billion
- Over 2,000 brands, including KitKat, Nescafé, Purina, Maggi, and Perrier.
Nestlé’s ability to adapt products to local markets while maintaining its global presence makes it one of the most powerful multinational corporations.
Key Takeaway:
- Localization + scale keeps Nestlé ahead of competitors.
- It ensures global penetration through acquisitions and product adaptation.
Challenges & Controversies: Has Nestlé’s Growth Come at a Cost?
Despite its success, Nestlé has faced criticism on several fronts:
❌ Water Privatization: Accused of exploiting water resources and bottling water in drought-affected regions.
❌ Infant Formula Scandal (1970s-80s): Faced backlash for aggressively marketing baby formula in developing nations.
❌ Sustainability Issues: Criticized for palm oil sourcing and plastic waste.
❌ Child Labor Allegations: Faced lawsuits over child labor in cocoa supply chains.
While these ethical concerns have affected Nestlé’s reputation, the company has made efforts to improve transparency and sustainability.
Key Takeaway:
- Nestlé navigates scandals but remains too powerful to be seriously affected.
- It uses sustainability initiatives and CSR campaigns to maintain its brand image.
The Future of Nestlé: What’s Next for the Food Giant?
Nestlé is now pivoting toward health and wellness as consumers demand:
✅ Plant-based foods (e.g., Garden Gourmet and Sweet Earth brands).
✅ Sustainable packaging (aiming for 100% recyclable materials by 2025).
✅ Functional beverages (expanding into collagen-infused and gut-health drinks).
✅ AI & Personalization (developing customized nutrition solutions).
The company is also doubling down on coffee, pet food, and nutrition science, seeing them as the future of its business model.
Key Takeaway:
- Nestlé is evolving beyond traditional food into nutrition, sustainability, and AI-driven food innovation.
- Acquisitions will continue to strengthen its dominance in high-growth sectors.
Final Thoughts: Why Nestlé Remains Unstoppable
✔ Massive Brand Portfolio – Nestlé owns over 2,000 brands, covering every category.
✔ Aggressive Acquisitions – It buys market leaders instead of competing.
✔ Global Scale & Local Adaptation – It customizes products to fit every market.
✔ Innovation in Nutrition & Sustainability – The shift toward health, wellness, and plant-based products ensures future dominance.
Despite ethical concerns, Nestlé remains the undisputed leader in the food and beverage industry, and its reign isn’t ending anytime soon.
Sources:
1. Nestlé Annual Report 2023
2. Nestlé Major Acquisitions
3. Nestlé’s Global Market Presence by Region
4. Nestlé’s Revenue by Product Category
5. Nestlé’s Leadership Changes
6. Challenges Facing Nestlé’s New CEO