Introduction
The global pear industry plays a vital role in the fruit sector, with production spanning multiple continents and a complex value chain that involves cultivation, processing, distribution, and consumption. Pears are a widely consumed fruit, valued for their nutritional benefits, versatility in culinary applications, and economic significance in many agricultural economies. This report provides an in-depth analysis of the global pear industry, covering key producing countries, leading companies, the value chain, trade dynamics, market trends, sustainability initiatives, and future outlook.
Global Pear Production
Top Pear-Producing Countries
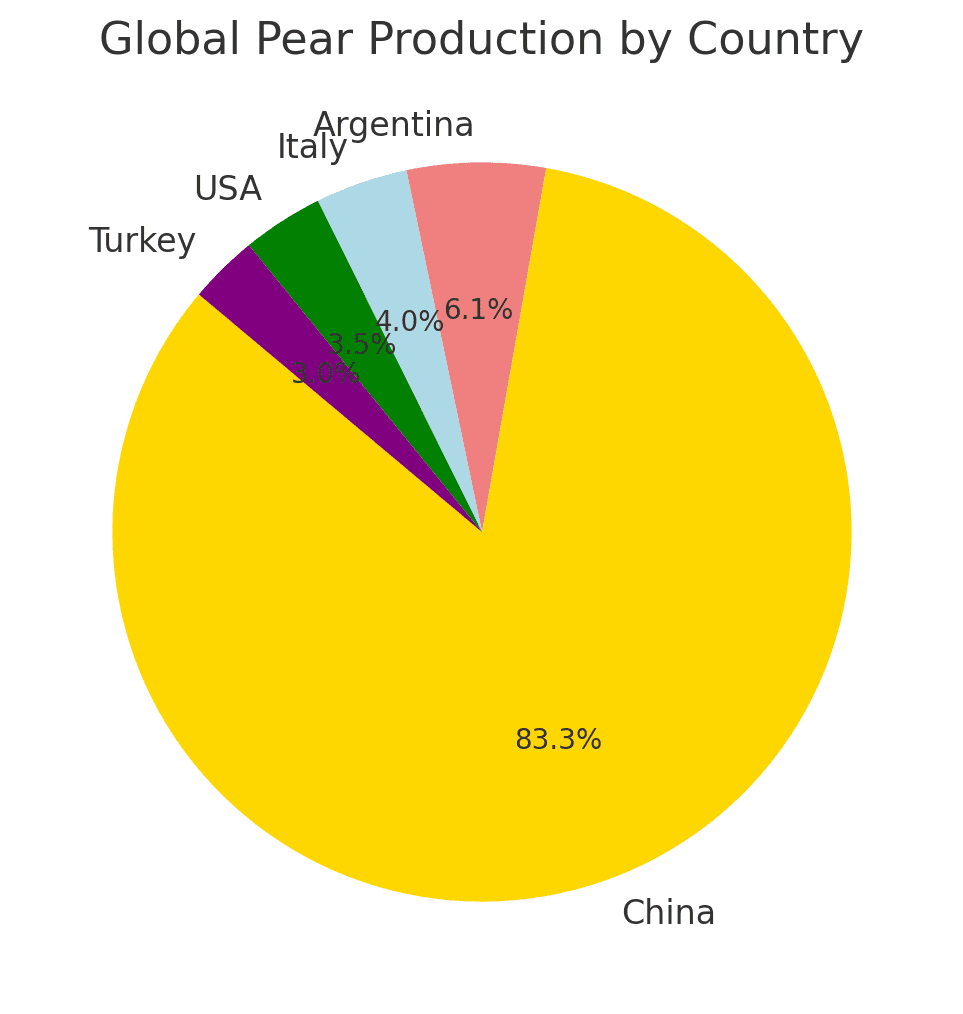
The leading producers of pears include China, Argentina, Italy, the United States, and Turkey. These countries have favorable climatic conditions for pear cultivation, supported by advanced farming techniques and extensive orchards.
- China – The world’s largest pear producer, accounting for nearly 65% of global production. Major pear-growing regions include Hebei, Shandong, and Shaanxi provinces.
- Argentina – A major exporter, known for its high-quality Bartlett and Packham pears. The Río Negro Valley is the primary production hub.
- Italy – Renowned for its premium pear varieties such as Abate Fetel and Williams. Emilia-Romagna is the leading pear-growing region.
- United States – Oregon and Washington dominate pear production in North America, with key varieties including Anjou, Bartlett, and Bosc.
- Turkey – A significant producer in Europe, cultivating a range of pear varieties, including Santa Maria and Williams.
Leading Pear Companies & Market Players
Several multinational and regional players influence the pear market through production, packaging, distribution, and retail.
- Dole Food Company – One of the largest fresh fruit companies, with extensive pear sourcing and distribution networks.
- Stemilt Growers – A leading U.S.-based grower and marketer specializing in organic and conventional pears.
- Zespri International – Known for its kiwi exports, but also involved in diversified fruit trade, including pears.
- Blue Whale Group – A France-based company with a strong presence in European pear markets.
- San Clemente Pears – A major South American player with a focus on high-quality exports to global markets.
Pear Value Chain: From Farm to Consumer
The pear industry comprises various interconnected stages:
- Cultivation & Harvesting – Pear orchards require specific climate conditions, proper irrigation, and pest control strategies. Harvesting is usually done manually to prevent bruising.
- Processing & Packaging – Post-harvest processes include sorting, washing, and waxing to enhance shelf life. Packaging is designed to protect pears during transportation.
- Distribution & Logistics – Pears are transported via refrigerated containers to maintain freshness. Cold storage facilities ensure proper temperature control throughout the supply chain.
- Retail & Consumption – Major supermarket chains, grocery stores, and online platforms play a key role in bringing pears to consumers worldwide.
Trade & Export Dynamics
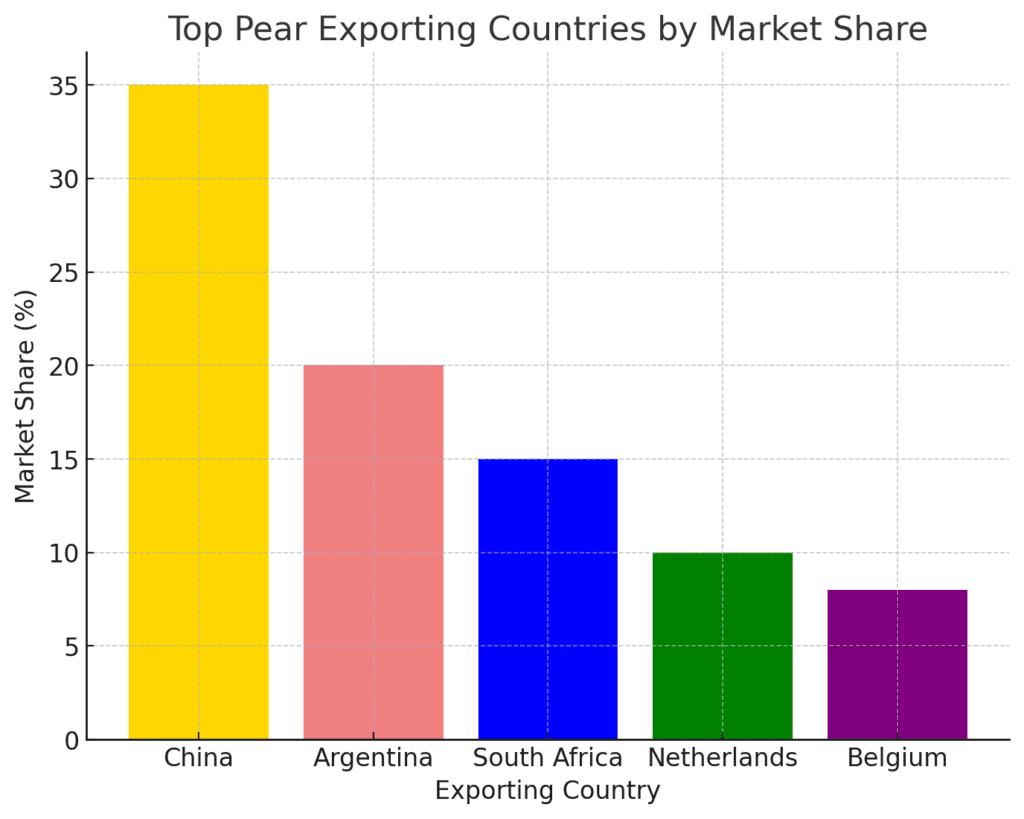
Top Exporting Countries
- China – Supplies fresh pears to markets across Asia, Europe, and North America.
- Argentina – A dominant exporter to the U.S. and European Union.
- South Africa – A key supplier to the Middle East and European markets.
Top Importing Countries
- United States – Imports large volumes of pears from South America and Europe.
- Germany – One of the leading pear consumers in Europe.
- Russia – A major destination for South American pears.
Trade regulations, tariffs, and phytosanitary requirements play a crucial role in global pear commerce, influencing pricing and supply chains.
Market Trends & Consumer Preferences
- Organic & Sustainable Pear Production – Growing demand for organic and non-GMO pears due to consumer awareness about health and environmental impact.
- Pear-Based Products – The rise of pear-infused beverages, dried pears, and pear-based skincare products.
- E-Commerce Expansion – Online grocery platforms driving direct-to-consumer sales for fresh pears.
- Regional Taste Preferences – Different varieties preferred in various markets, such as Anjou in the U.S. and Abate Fetel in Italy.
Sustainability & Challenges in the Pear Industry
Climate Change & Its Impact
- Unpredictable weather patterns and rising temperatures affect pear yield and quality.
- Innovations in smart irrigation systems and climate-resistant cultivars are helping mitigate risks.
Sustainable Farming Practices
- Organic pear farming, reducing pesticide use.
- Water-efficient irrigation techniques to conserve resources.
Future Outlook
- Technological Advancements – AI and precision farming are revolutionizing pear production efficiency.
- Market Expansion – Emerging economies in Asia and Africa offer growth potential for pear imports.
- Health & Nutrition Trends – Increased focus on pears as a functional food with health benefits.
The pear industry continues to evolve, shaped by technological innovation, consumer demand, and global trade dynamics. As sustainability and quality remain focal points, producers and market players must adapt to changing trends for long-term growth.



