Introduction: Why Soybeans Matter in the Modern World
Soya has become a strategic commodity for the 21st century. Beyond its role in global cuisine, soy supports sustainable farming, powers industrial innovation, and delivers health benefits. This guide explores the comprehensive applications of soybeans across food, animal feed, cosmetics, nutraceuticals, and industry.
🕯️ G Rose Soy Candles
Hand-poured in Cape Town, G Rose Soy Candles offers beautifully crafted essential oil massage candles and French-scented soy wax melts. Sustainably made, toxin-free, and infused with elegance—perfect for conscious consumers who appreciate both wellness and atmosphere.
💝 Explore their range of luxury gifts, wellness scents, and handmade creations at g-rose.co.za
📸 Follow them on Instagram @g_rose_soycandles
Food and Beverage Applications of Soy
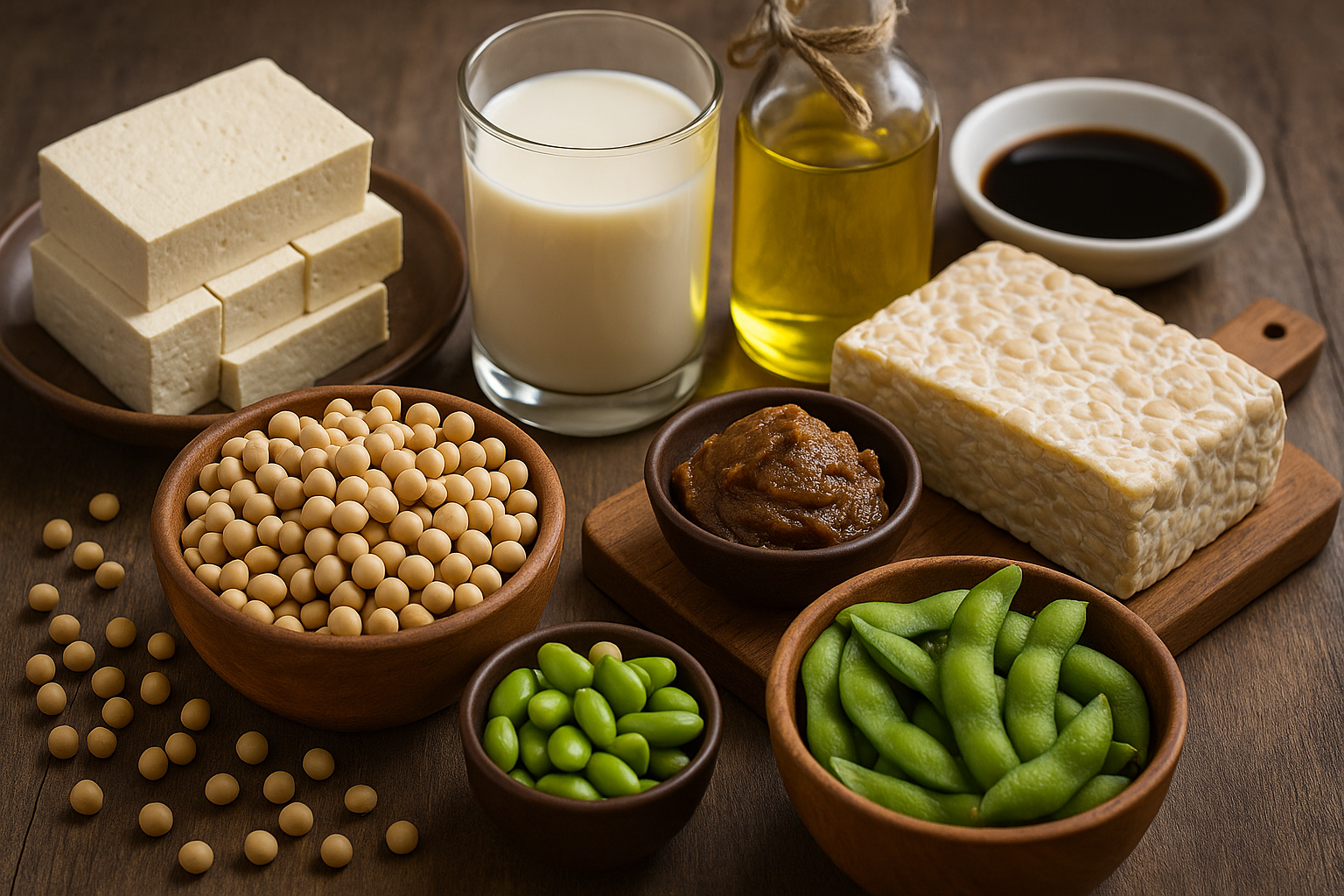
Soya has deep culinary roots, particularly in Asia, and has now become a global staple in many diets. Key soy food products include:
- Tofu
- Soy milk
- Tempeh
- Miso
- Soy sauce
- Edamame
- Soy flour & TVP (Textured Vegetable Protein)
Soy derivatives like soy lecithin are added to everything from chocolate to salad dressings to ensure smooth textures and shelf stability.
Soybean oil is a dominant edible oil, comprising over 54% of the U.S. vegetable oil market. It’s commonly labeled as “vegetable oil” and used for frying and baking. It is low in saturated fat and contains heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E. The FDA permits a qualified health claim linking daily soybean oil consumption to reduced coronary heart disease risk.
Soy milk, fortified with calcium and protein, is a key dairy alternative for the lactose intolerant. Tofu absorbs flavors and serves as a plant-based protein centerpiece in many diets. Fermented soy products like tempeh, miso, and soy sauce offer umami flavor and digestive benefits. Edamame, or green soybeans, is a high-fiber, protein-rich snack.
Soy protein is “complete,” containing all nine essential amino acids. It’s cholesterol-free and rich in antioxidants and polyunsaturated fats, making it ideal for plant-based diets.
Animal Feed and Agricultural Uses of Soy
Globally, over 75% of soybeans are used in livestock feed—especially for poultry, pigs, and cattle.
- Soybean meal, a by-product of oil extraction, contains about 50% protein.
- 97% of global soybean meal is used for animal feed.
- In the U.S., 70% of domestic soy is animal feed. Breakdown: Poultry (67%), Swine (21%), Cattle (10%).
Sustainable Agriculture
Soybeans improve soil health through nitrogen fixation, thanks to their relationship with rhizobium bacteria. Crop rotation with soybeans reduces fertilizer use and boosts yields in crops like corn.
Soy hulls are used in cattle rations for fiber. Soy straw can be repurposed for bedding or plowed back into soil as organic matter. Soy literally feeds the world twice: through animals and directly through soy-based foods.
Global Production and Trade
Soybeans are a top global commodity. Leading producers include:
- Brazil – the largest producer and exporter.
- United States – previously the largest exporter.
- Argentina, China, and India follow.
Trade tensions, such as U.S.-China tariffs, directly impact global prices. Deforestation concerns in Brazil have brought scrutiny to sustainable sourcing.
Nutraceuticals and Health Benefits of Soy
Soy shines in the nutraceuticals sector, offering health-supporting compounds like:
- Isoflavones (genistein and daidzein)
- Lecithin
- Soy protein isolates and concentrates
Functional Benefits:
- Soy protein is used in powders, bars, and meal replacements.
- The FDA recognizes that 25g/day of soy protein, when part of a low saturated fat diet, may reduce heart disease risk.
- Isoflavones may reduce menopausal symptoms, improve bone density, and protect skin.
- Soy lecithin supports brain, liver, and fat metabolism.
- Fermented soy products like natto contain nattokinase, linked to heart and circulation health.
Soy-based supplements and functional foods help consumers meet specific health goals—ranging from cardiovascular support to muscle building.
Cosmetics and Personal Care Uses
Soy is widely used in personal care for its skin- and hair-friendly properties.
Key Ingredients:
- Soybean oil (Glycine soja oil): Rich in linoleic acid and vitamin E; moisturizes and softens skin.
- Soy lecithin: Acts as an emulsifier and skin conditioner.
- Hydrolyzed soy protein: Enhances hair strength and shine.
Cosmetic Benefits:
- Non-comedogenic, suitable for sensitive skin.
- Found in facial cleansers, shampoos, moisturizers, serums, and makeup removers.
- Total Soy Complex, used in AVEENO® products, brightens and evens skin tone.
- Genistein, a soy isoflavone, boosts collagen and elasticity, combats photo-aging.
Soy is also used in natural deodorants, lip balms, and vitamin E supplements, making it a multifunctional and sustainable cosmetic ingredient.
Industrial and Environmental Applications of Soy
Soybeans are revolutionizing industry with sustainable alternatives to petrochemicals.
Biofuels
- Soy biodiesel accounts for 31% of U.S. soybean oil use.
- Reduces lifecycle GHG emissions by up to 86%.
- Used in farm equipment, trucks, heating systems, and being explored for aviation fuel.
Other Industrial Uses:
- Soy adhesives: Low-VOC alternatives to formaldehyde in wood products.
- Soy inks: Used in newspapers and packaging; easier to recycle.
- Soy lubricants: Biodegradable and ideal for marine/agricultural use.
- Soy foams: Used by Ford in car seats; by Goodyear in tires; by Skechers in shoes.
- Soy polyols: Applied in bioplastics, foams, and insulation.
- Asphalt sealants: High-oleic soy oil rejuvenates roads, enabling higher recycled content and better durability.
- Soy wax: Popular in eco-friendly candles.
Soy supports green manufacturing at scale—backed by major brands like John Deere, Case IH, and Goodyear.
Challenges and Controversies Around Soy
Despite its many benefits, soy is not without scrutiny:
- GMO soy: Over 90% of soy in the U.S. is genetically modified; this raises consumer concerns.
- Deforestation: Particularly in Brazil’s Cerrado and Amazon regions for soybean expansion.
- Hormonal effects: Isoflavones are phytoestrogens, which spark myths about feminizing effects—though science shows no significant risk in typical dietary amounts.
- Soy allergies: Common among children, but often outgrown.
Consumers are increasingly demanding non-GMO, organic, or certified sustainable soy.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations in Soy
Soy is part of the innovation frontier:
- Bioplastics: Soy-based polymers for packaging.
- Soy-based medical materials: Used in tissue scaffolding and controlled-release drug carriers.
- Smart coatings and adhesives: Derived from soy polyols.
- Eco electronics: Research into soy components in biodegradable circuits.
Soy continues to adapt to evolving environmental and technological demands.
Conclusion: Soy’s Cross-Sector Importance
Soybeans are more than just food—they’re a cornerstone of sustainable business.
For manufacturers, soy provides a cost-effective, renewable input across food, agriculture, beauty, and industry. For consumers, soy enhances nutrition, offers eco-friendly choices, and supports health and wellness. For the planet, soy helps reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promotes regenerative agriculture.
From tofu to tires, biodiesel to skincare, soy powers modern life. As global demand for plant-based and eco-conscious solutions rises, soy is poised to lead the way—feeding people, supporting farmers, fueling industries, and protecting the planet.
References:
1.Wikipedia – Soybean: Overview of soybean uses in food, feed, and industry .
2.U.S. Soy (United Soybean Board) – What Are Soybeans Used For? (2018): Breakdown of soy uses in food vs. feed vs. industrial products .
3.Our World in Data – Drivers of Deforestation (2021): Global soy allocation (~77% to animal feed, <10% to direct food) .
4.Oklahoma Soybean Board – Soybean Uses: Statistics on animal feed usage (species breakdown) and food oil usage .
5.Kentucky Food & Farm – Soy Many Uses! (2022): Examples of soy in foods (oil, lecithin) and industrial innovations (biodiesel, tires, asphalt, etc.) .
6.NCCIH – Soy: Usefulness and Safety: Notes that soy supplements (protein, isoflavones) are used for cholesterol, menopause, etc., with evidence of modest benefits .
7.U.S. FDA (via USB) – Recognized heart health claim for soy protein (25g/day may reduce heart disease risk) and qualified claim for soybean oil (unsaturated fat benefits) .
8.U.S. Soy – Nine Reasons Why Soybean Oil is Good for Your Skin (2024): Highlights of soybean oil in skincare (rich in fatty acids, vitamin E, moisturizing properties) .
9.KyFoodandFarm – Personal care products with soy (Aveeno soy complex, soy in shampoos/soaps, etc.) .
10.British J. of Pharmacology – Genistein and Skin Aging (2012): Found soy isoflavone genistein improved skin elasticity and reduced aging signs in studies .
11.ScienceDirect – Industrial Uses for Soybeans: Overview of soy in adhesives, plastics, fibers, and coatings .
12.United Soybean Board – Soy New Uses (2020): Soy-based products guide with 1000+ items from flooring to personal care, demonstrating soy’s expanding industrial role .
