
Introduction
China, the world’s most populous country, is also one of the largest producers of corn (maize). Corn is a vital crop in China’s agricultural landscape, used extensively in food production, animal feed, and industrial applications. As the demand for maize continues to rise, both domestically and globally, China plays a central role in the global corn market. The country is not only a major producer but also a significant importer and exporter of corn, thanks to its vast agricultural sector and robust trade infrastructure.
In this report, we explore the key aspects of China’s corn production industry, highlighting its growth, production regions, leading companies, challenges, and future opportunities. We also examine China’s role in the global corn supply chain and its plans for increasing productivity and sustainability in the future.
The Role of Corn in China’s Agriculture
Corn is one of China’s staple crops, second only to rice in terms of production. It is used in various sectors, including food, animal feed, and biofuels. The growth of China’s livestock industry, particularly in poultry and pork, has led to a substantial increase in demand for corn as animal feed. Additionally, corn is used as a key ingredient in the production of starch, syrups, and oils, as well as in the growing biofuel industry.
Key uses of corn in China:
- Animal Feed: With a rapidly growing livestock industry, China’s demand for corn as animal feed has soared. Corn is a major component in poultry, swine, and cattle feed.
- Food Production: Corn is used in various food products, such as cornmeal, corn oil, and snacks, catering to both domestic consumption and international markets.
- Industrial Applications: Corn is a primary raw material in the production of starch, corn syrup, and ethanol. The increasing demand for biofuels has further bolstered corn production in China.
- Biofuels: Corn is a key feedstock for ethanol production, which supports China’s ambitions to enhance its renewable energy capacity.
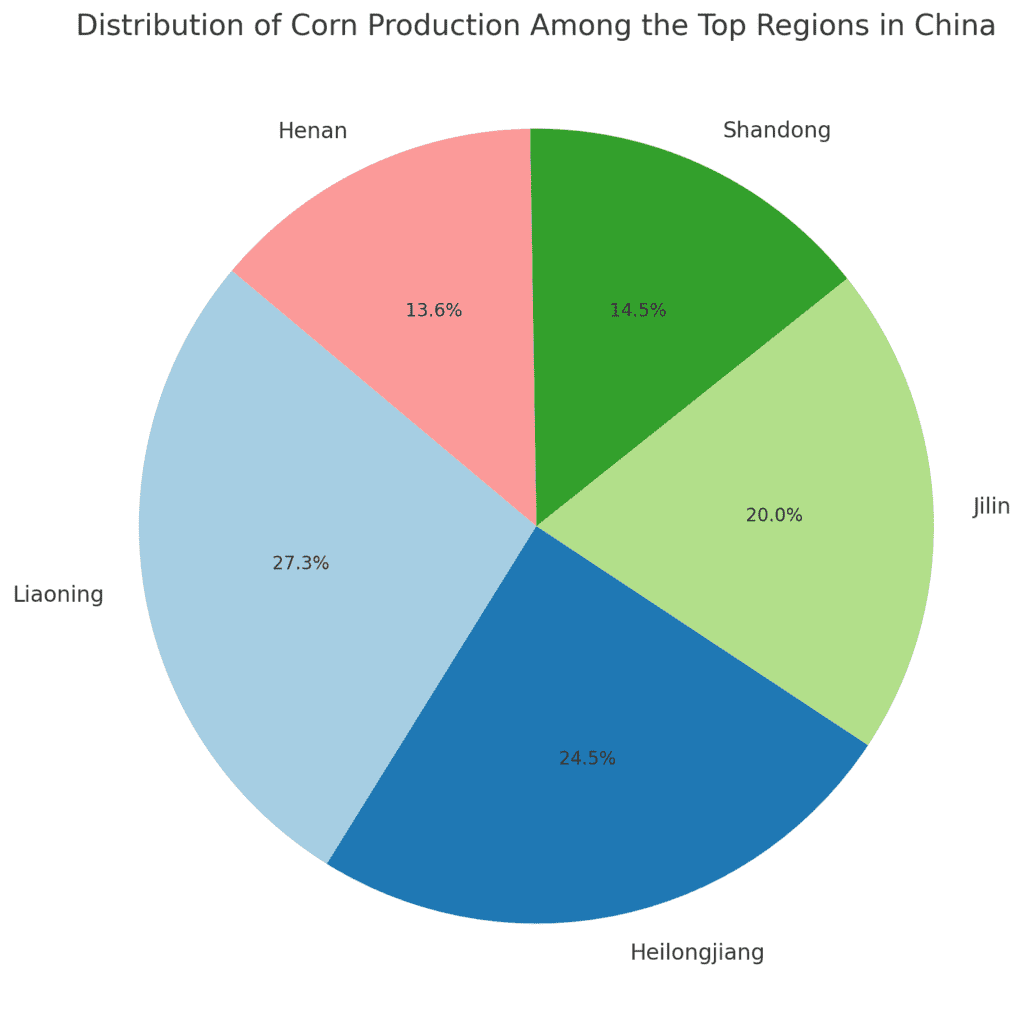
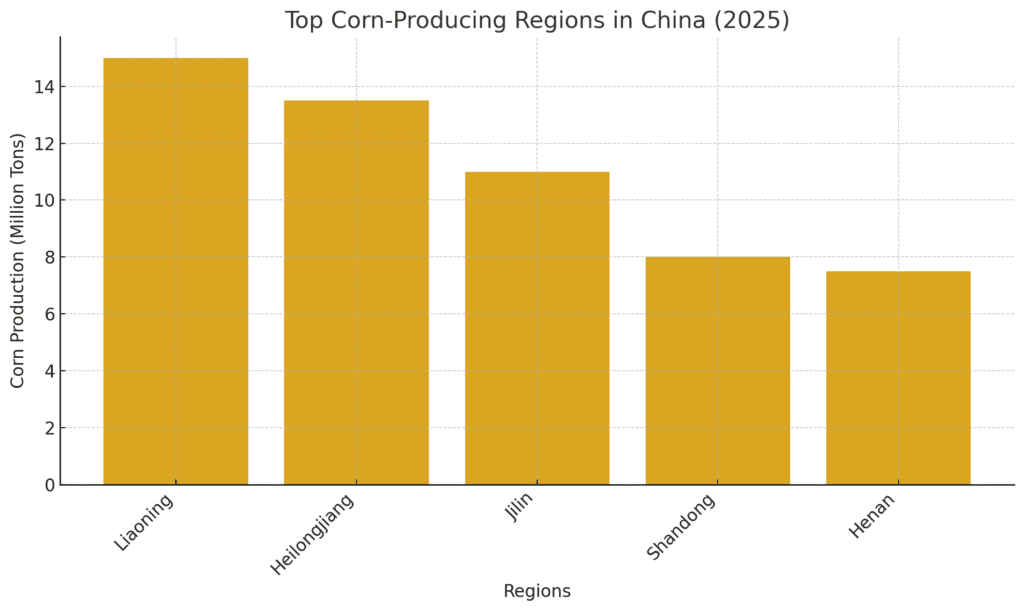
Key Corn-Producing Regions in China
China’s vast agricultural landscape is divided into several major corn-growing regions, each contributing significantly to the country’s overall maize output. These regions benefit from favorable climatic conditions and efficient farming practices, allowing for high yields of corn.
1. Liaoning
Liaoning, located in northeastern China, is one of the country’s largest corn-producing provinces. The fertile soils and moderate climate make it an ideal region for corn cultivation. Liaoning’s maize is primarily used for both domestic consumption and animal feed production. The province also plays a key role in exporting corn to other regions of China and abroad.
Key Facts:
- Leading corn producer in northeastern China
- Focuses on food-grade and feed corn
- Major contributor to both domestic and export markets
2. Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang, another major corn-growing province in northeastern China, is known for its high maize yields. The province benefits from vast plains and favorable growing conditions, making it one of the largest producers of corn in China. Heilongjiang’s corn is used in various sectors, including animal feed, food processing, and biofuels.
Key Facts:
- High corn yields in the northeastern plains
- Key player in both domestic markets and exports
- Significant supplier of corn for food, feed, and biofuels
3. Jilin
Jilin, located in the northeast, is one of China’s key agricultural provinces for corn production. The region is known for its high-quality maize, which is used in both food production and animal feed. Jilin’s corn production has grown rapidly due to improvements in farming practices and technology.
Key Facts:
- Significant player in northeast China’s corn production
- Known for high-quality corn used in food and feed
- Advances in farming technology and practices boosting yields
4. Shandong
Shandong is one of China’s top agricultural provinces, with a substantial portion of its farmland dedicated to corn production. The province is known for its advanced irrigation systems and adoption of modern farming techniques, which help increase corn yields. Shandong is a major supplier of corn to other regions in China, and its corn is used for food processing, animal feed, and industrial applications.
Key Facts:
- Major contributor to China’s corn supply
- Focus on food processing, feed, and industrial uses
- Strong infrastructure for irrigation and farming technology
5. Henan
Henan, located in central China, is one of the country’s largest corn-producing provinces. It is home to extensive farmland dedicated to maize cultivation, benefiting from its moderate climate and soil fertility. Henan produces both food-grade and feed corn, with a significant portion used in the domestic food industry.
Key Facts:
- One of the top corn producers in central China
- Focus on both food-grade and animal feed maize
- Known for its agricultural infrastructure and innovation
Leading Companies in China’s Corn Industry
Several companies play a significant role in China’s corn production and processing sectors. These companies contribute to the country’s overall maize supply, with operations spanning farming, processing, and distribution.
1. COFCO Corporation
COFCO is one of China’s largest state-owned food companies and a leading player in the corn industry. The company is involved in corn trading, processing, and biofuel production. COFCO also operates large-scale corn farms and has a strong presence in both the domestic and international maize markets.
Key Facts:
- Major player in corn trading and processing
- Focus on food, feed, and biofuel production
- Extensive export network and logistics infrastructure
2. China National Chemical Corporation (ChemChina)
ChemChina, through its subsidiary Sinochem International, plays a key role in China’s corn industry, particularly in the production of corn-based industrial products such as starch and ethanol. The company is also involved in corn farming and has a significant presence in China’s agricultural sector.
Key Facts:
- Focus on corn-based industrial products like starch and ethanol
- Strong presence in China’s maize production and processing
- Significant role in China’s biofuel sector
3. Shandong Weifang Yaxing Chemical
Shandong Weifang Yaxing Chemical is one of the leading companies in the corn processing industry in China. The company produces a wide range of products from corn, including starch, syrups, and ethanol. Shandong Weifang Yaxing Chemical is a key supplier of industrial corn products in China.
Key Facts:
- Major producer of corn-based industrial products
- Focus on starch, syrups, and ethanol production
- Key player in China’s corn processing industry
4. Xinjiang Tianye Group
Xinjiang Tianye Group is a significant player in China’s corn industry, with a focus on both farming and corn-based product manufacturing. The company is involved in corn production, starch production, and biofuel manufacturing, playing an important role in meeting China’s domestic corn demand.
Key Facts:
- Involved in both corn farming and processing
- Focus on starch and biofuel production
- Plays a key role in China’s maize supply chain
Challenges Facing China’s Corn Industry
While China’s corn industry is large and growing, there are several challenges that could impact its future growth:
1. Climate Change
China’s corn production is highly dependent on favorable weather conditions. Climate change, including rising temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns, could negatively affect crop yields and farming efficiency.
2. Price Volatility
Corn prices in China can fluctuate due to factors like global supply and demand, government policies, and market speculation. These fluctuations can impact farmers’ ability to predict income and manage production costs.
3. Land Fragmentation
Many small-scale farmers in China have fragmented landholdings, which can limit their ability to adopt modern farming technologies. Larger agribusinesses have a competitive advantage due to economies of scale.
Future Opportunities in China’s Corn Industry
Despite these challenges, several opportunities exist for growth in China’s corn industry:
1. Increased Demand for Animal Feed
The growing demand for poultry, pork, and dairy products in China presents a significant opportunity for corn producers. As the livestock sector expands, the need for corn as animal feed is expected to increase.
2. Biofuel Expansion
As China continues to prioritize renewable energy, the demand for corn in biofuel production, particularly ethanol, is expected to grow. The government’s policies to promote biofuels create a strong market for maize.
3. Adoption of Modern Farming Techniques
The widespread adoption of precision farming, improved irrigation systems, and better crop management technologies can help boost corn yields, making China’s maize production more sustainable and efficient.
Conclusion
China’s corn industry plays a critical role in its agricultural sector and the global corn market. With vast agricultural land, favorable growing conditions, and a growing demand for corn in food, animal feed, and biofuels, China is well-positioned to continue its leadership in corn production. However, challenges such as climate change, price volatility, and land fragmentation need to be addressed. By embracing modern technologies and sustainable practices, China’s corn industry can continue to thrive and meet the growing demand for maize both domestically and globally.


