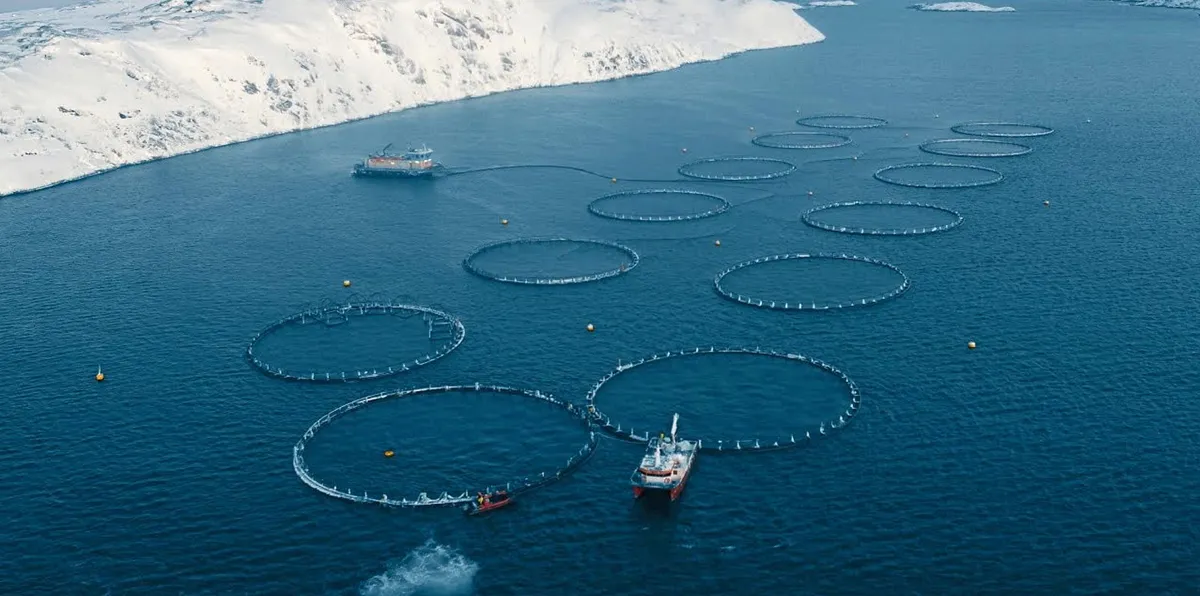
The salmon farming sector has experienced a significant decline, marking the largest decrease in the industry. This downturn has raised concerns and prompted stakeholders to closely examine the factors contributing to this decline.
Several factors have been identified as potential causes for the decline in the salmon farming sector. One of the primary factors is the impact of environmental changes and challenges. Climate change, in particular, has had a significant impact on the salmon farming industry. Rising sea temperatures, changing ocean currents, and other environmental factors have disrupted the delicate balance necessary for successful salmon farming operations.
In addition to environmental challenges, the salmon farming sector has also faced a number of regulatory and market-related challenges. Changing regulations, trade policies, and consumer preferences have all played a role in shaping the current landscape of the industry. These factors have created a complex and challenging environment for salmon farmers, leading to a decline in production and profitability.
The decline in the salmon farming sector has had far-reaching implications for both the industry and the broader economy. Salmon farming is a major economic driver in many regions, providing jobs, income, and economic stability to local communities. The decline in this sector has not only impacted salmon farmers and their employees but has also had ripple effects throughout the supply chain and beyond.
To address the challenges facing the salmon farming sector, stakeholders must work together to develop sustainable solutions that support the long-term viability of the industry. This will require collaboration between government agencies, industry leaders, environmental organizations, and other key stakeholders to identify and implement strategies that promote the health and sustainability of salmon farming operations.
One potential solution to the challenges facing the salmon farming sector is the development of innovative technologies and practices that can help mitigate the impact of environmental changes and improve overall efficiency and sustainability. This could include the use of advanced monitoring and data analytics tools to better understand and respond to changing environmental conditions, as well as the development of new aquaculture techniques that minimize the environmental footprint of salmon farming operations.
In addition to technological innovations, efforts to improve transparency and accountability within the salmon farming industry can also help rebuild consumer trust and support the long-term sustainability of the sector. By implementing robust traceability systems, certification programs, and other initiatives that promote responsible and ethical practices, salmon farmers can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and social responsibility.
Furthermore, investments in research and development, education, and training can help build the capacity and expertise needed to address the challenges facing the salmon farming sector. By supporting the development of skilled professionals, promoting knowledge exchange, and fostering innovation, stakeholders can help ensure the long-term success and sustainability of the industry.
Ultimately, the decline in the salmon farming sector serves as a wake-up call for stakeholders to come together and take action to address the challenges facing the industry. By working collaboratively to develop and implement sustainable solutions, stakeholders can help ensure the continued viability of salmon farming operations and support the economic, social, and environmental well-being of the communities that rely on this important industry.