
The global poultry industry is poised for significant growth in 2025, with projections indicating an expansion of approximately 2.5% to 3%. This growth is driven by factors such as poultry’s affordability, increasing consumer demand, and its relatively lower environmental impact compared to other meats. However, the industry faces challenges including avian influenza outbreaks, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions. A comprehensive understanding of the poultry value chain—from production to consumption—is essential for stakeholders aiming to navigate this dynamic landscape effectively.
1. Introduction
Poultry, encompassing chickens, turkeys, ducks, and other birds, plays a crucial role in global agriculture and food systems. Its popularity stems from its cost-effectiveness, nutritional value, and versatility in culinary applications. In 2025, the industry is expected to continue its upward trajectory, supported by favorable market conditions and evolving consumer preferences.
2. Global Market Overview
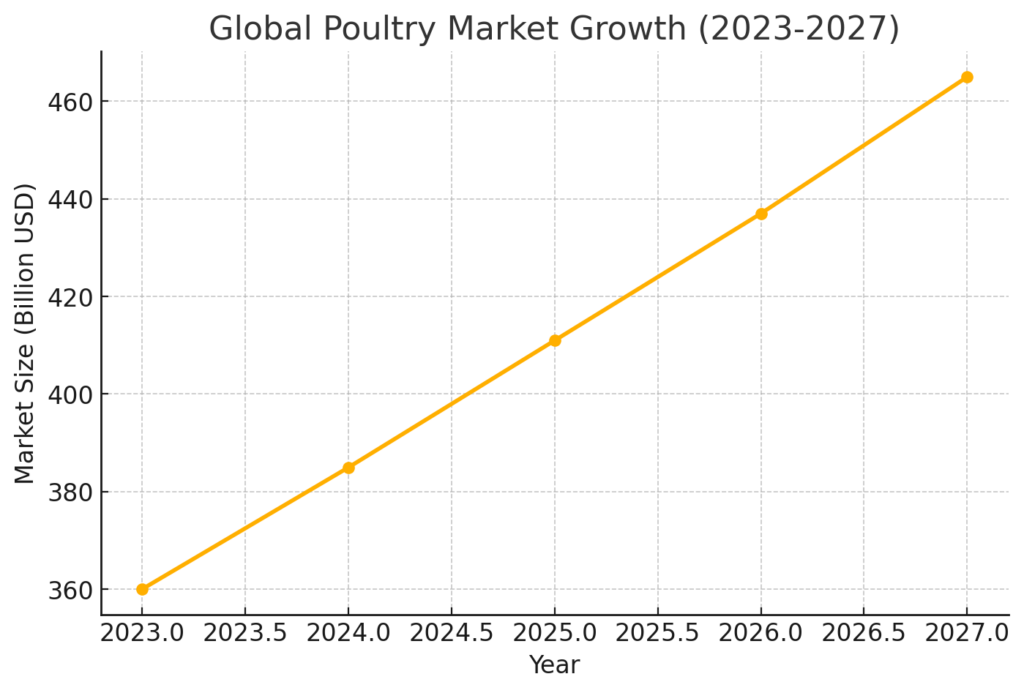
The poultry market is projected to grow from $384.95 billion in 2024 to $410.98 billion in 2025, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.8%. This growth is attributed to rising meat consumption, economic development in emerging markets, and increased awareness of poultry’s health benefits.
thebusinessresearchcompany.com
3. Poultry Value Chain Analysis
The poultry value chain comprises several interconnected stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality, safety, and availability.
3.1. Breeding and Hatchery
This initial stage involves selecting and breeding parent stock to produce high-quality chicks. Advancements in genetics and breeding techniques have led to improved growth rates, feed conversion ratios, and disease resistance. However, the global supply of breeding stock has faced challenges due to avian influenza outbreaks, necessitating stringent biosecurity measures.
3.2. Feed Production
Feed constitutes a significant portion of production costs. The industry has seen a shift towards precision nutrition, utilizing enzymes, probiotics, and tailored feed formulations to enhance efficiency and sustainability. The precision poultry nutrition market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.0% to 6.5% from 2025 to 2030.
3.3. Farming and Production
Poultry farming ranges from small-scale backyard operations to large commercial enterprises. Technological advancements, such as automated feeding systems and environmental controls, have improved productivity. However, disease management, particularly concerning avian influenza, remains a critical concern. Vaccination and enhanced biosecurity protocols are essential to mitigate risks.
3.4. Processing and Packaging
Processing involves slaughtering, cleaning, and packaging poultry products. The global meat and poultry processing equipment market is projected to grow from $12.73 billion in 2024 to $13.89 billion in 2025, indicating a CAGR of 9.1%. This growth is driven by increased demand for processed products and advancements in processing technologies.
3.5. Distribution and Retail
Efficient distribution networks ensure that poultry products reach consumers in optimal condition. The rise of e-commerce and changes in consumer purchasing behavior have prompted companies to invest in cold chain logistics and online retail platforms. Supermarkets, hypermarkets, and food service outlets remain primary distribution channels.
thebusinessresearchcompany.com
3.6. Consumption
Consumer preferences are shifting towards leaner meats and sustainably produced foods. Poultry’s lower carbon footprint compared to other meats makes it an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers. Emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are experiencing significant increases in poultry consumption due to urbanization and rising incomes.
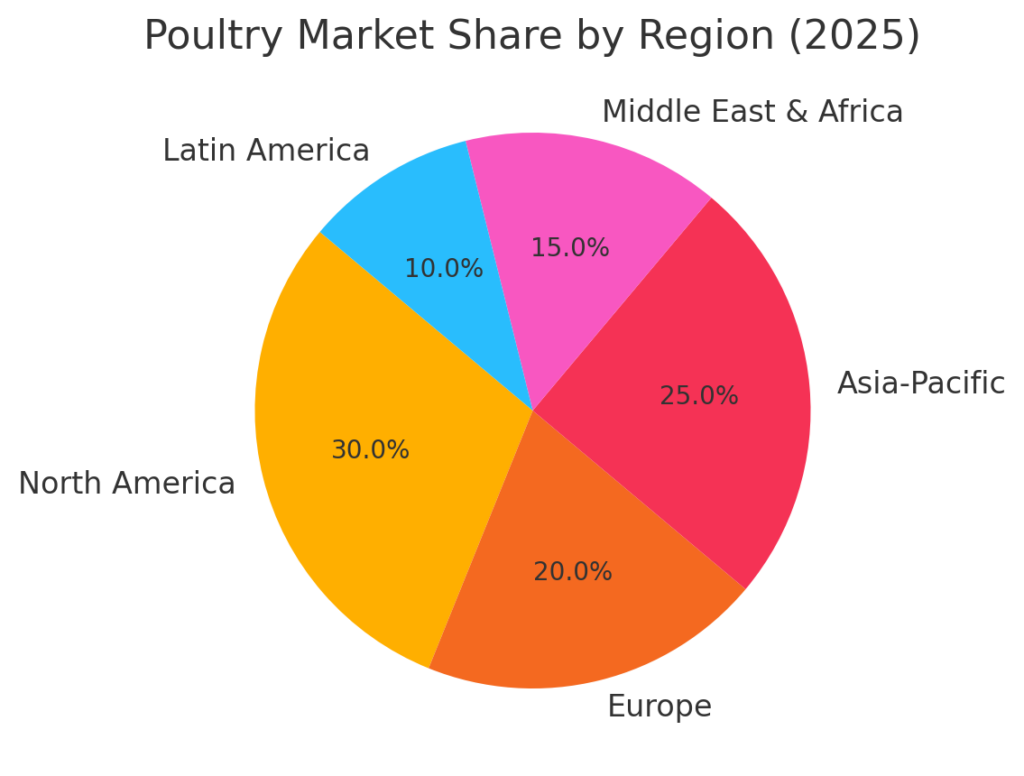
4. Regional Insights
4.1. North America
The U.S. poultry industry is the world’s largest producer and second-largest exporter of poultry meat. In 2022, nearly 15% of poultry meat produced in the U.S. was exported. The industry is influenced by currency fluctuations, trade negotiations, and economic growth in importing markets.
4.2. Europe
Europe has seen ongoing growth in poultry consumption, with a focus on sustainability and animal welfare. The region is currently outpacing global market growth, driven by increased preference for poultry and strong marketing and product development efforts.
4.3. Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the precision poultry nutrition market, representing 25% to 30% of the market. Rapid expansion of poultry farming in China, India, and Southeast Asia is driving a CAGR of 6.0% to 7.0%.
4.4. Middle East and Africa
The Middle East and Africa are expected to lead growth in the poultry industry, with significant increases in production and consumption. These regions are experiencing rapid urbanization and rising incomes, which are driving higher demand for poultry meat.
5. Challenges and Risks (Continued)
5.2. Geopolitical Tensions
Geopolitical tensions and trade issues will continue to challenge the global poultry industry, impacting supply chains, market access, and input costs. Some of the key geopolitical factors affecting the poultry sector in 2025 include:
- U.S.-China Trade Relations: Ongoing disputes between the United States and China have led to fluctuations in import-export policies, including tariffs on poultry products. The U.S. remains a significant supplier of poultry to China, but trade restrictions could impact market stability.
- Russia-Ukraine Conflict: The ongoing conflict has disrupted grain supplies, particularly wheat and corn, which are essential feed ingredients for poultry farming. This has led to increased feed costs and supply chain delays in many regions.
- Brazil’s Poultry Export Dominance: As the world’s largest poultry exporter, Brazil continues to expand its market presence. However, concerns about deforestation and sustainability in Brazilian agriculture have led some markets, particularly in Europe, to impose stricter import regulations.
- EU and UK Trade Policies: The European Union and the United Kingdom have implemented more stringent health and safety regulations for imported poultry, which could affect trade relations with major poultry-producing nations like the U.S., Brazil, and Thailand.
Geopolitical instability creates an unpredictable market environment, affecting not only trade flows but also investment in poultry infrastructure and global supply chain efficiency.
6. Key Industry Trends and Innovations
The poultry industry in 2025 is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, sustainability efforts, and changing consumer preferences. Here are some key trends shaping the market:
6.1. Sustainability and Animal Welfare
Consumers are increasingly demanding ethically sourced and sustainable poultry products. As a result:
- Alternative Feeds: There is a growing shift toward alternative protein sources such as insect-based feeds, algae, and fermented proteins to reduce the environmental impact of soy and corn production.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: Poultry producers are implementing energy-efficient processing methods, water recycling systems, and renewable energy sources.
- Improved Living Conditions: The shift toward free-range, cage-free, and organic poultry farming continues to gain traction, particularly in Europe and North America.
6.2. Automation and Smart Farming
The integration of AI, IoT, and blockchain technology is enhancing efficiency across the poultry supply chain:
- AI-Driven Monitoring Systems: Smart sensors and cameras analyze bird health, feed intake, and behavior to optimize growth and detect early signs of disease.
- Automated Processing Plants: Robotics and AI-driven processing lines reduce labor dependency and improve precision in slaughtering, deboning, and packaging.
- Blockchain for Transparency: Blockchain technology is being used for traceability in the poultry supply chain, ensuring that consumers and retailers can verify the source of their poultry products.
6.3. Rise of Alternative Poultry Proteins
The emergence of lab-grown and plant-based poultry substitutes is disrupting traditional poultry markets. While these alternatives are not yet a significant threat to conventional poultry, they are gaining momentum due to:
- Health-conscious consumers seeking lower cholesterol and antibiotic-free options.
- Environmental advocates pushing for reduced carbon emissions in meat production.
- Major investments from food-tech companies and venture capital firms.
6.4. Expansion of E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Sales
The way consumers purchase poultry products is changing. Online poultry sales are expected to grow by 12-15% annually, driven by:
- The rise of meal kits and subscription services that offer premium poultry cuts.
- E-commerce platforms like Amazon Fresh and Walmart+, which provide fresh poultry deliveries.
- Cold-chain logistics advancements, ensuring longer shelf life and safe transportation.
7. Challenges and Risks in the Poultry Industry
Despite positive growth projections, the poultry industry faces several challenges that could impact profitability and sustainability.
7.1. Avian Influenza and Disease Outbreaks
- The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) remains a major threat, with outbreaks leading to mass culling of poultry and export bans.
- Governments are increasing biosecurity regulations, and some regions are considering mandatory vaccinations to prevent further outbreaks.
7.2. Geopolitical and Trade Barriers
- Tariffs and import bans on poultry products have disrupted international trade.
- Russia-Ukraine war and U.S.-China tensions continue to impact feed ingredient prices, particularly for soy and corn.
- Poultry exports from Brazil and the U.S. dominate the global market, but political factors can affect trade relations.
7.3. Rising Costs of Production
- Feed costs make up 60-70% of total poultry production expenses, and volatile grain prices (due to climate change and supply chain disruptions) are a growing concern.
- Energy costs for cold storage, processing, and transportation are increasing, affecting overall profitability.
7.4. Labor Shortages
- Poultry farms and processing plants are experiencing workforce shortages, particularly in North America and Europe, leading to higher wages and automation investments.
- Strict labor laws and working conditions scrutiny are pushing companies to focus on automation and robotics.
8. Future Outlook: The Poultry Industry Beyond 2025
The poultry industry is expected to continue growing over the next five years, with notable developments shaping its trajectory:
8.1. Increased Regional Production
- Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa will see accelerated poultry production growth to meet domestic demand.
- China and India are projected to become major poultry exporters, challenging the dominance of Brazil and the U.S.
8.2. Government and Regulatory Shifts
- Governments worldwide are tightening animal welfare laws, leading to a move away from intensive poultry farming.
- Food safety regulations on antibiotic use and poultry processing methods are increasing, particularly in Europe and the U.S..
8.3. Technological Breakthroughs
- AI-powered poultry management systems will become standard, reducing disease risks and optimizing feed efficiency.
- Gene-editing technologies like CRISPR could be used to develop disease-resistant poultry breeds.
8.4. Sustainability-Driven Investments
- Investors are looking for low-carbon poultry production solutions, favoring companies with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) initiatives.
- Companies that focus on circular economy principles, such as utilizing waste by-products for fertilizer or biofuels, will gain a competitive edge.
9. Key Takeaways for Industry Players
For farmers, processors, retailers, and policymakers, staying competitive in the evolving poultry landscape requires:
- Investing in sustainable and ethical poultry production to meet consumer demands and regulatory requirements.
- Adopting digital technologies, AI, and automation to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Strengthening biosecurity measures to mitigate disease risks.
- Diversifying supply chains to reduce dependency on high-cost feed imports.
- Capitalizing on the e-commerce boom by expanding direct-to-consumer poultry sales.
10. Final Conclusion
The poultry industry in 2025 remains a key pillar of global food security, with its affordability, nutritional value, and adaptability driving continuous growth. However, industry players must navigate challenges such as disease outbreaks, rising costs, and shifting consumer expectations. By leveraging technology, sustainability practices, and market diversification, businesses can ensure long-term profitability and resilience in an increasingly competitive global market.

