
Introduction
Grapes are among the most widely cultivated fruits globally, with applications in fresh consumption, wine production, juice processing, and dried fruit industries. The grape industry plays a crucial role in the agricultural economy, contributing significantly to international trade. This report provides a detailed analysis of the global grape industry, covering production, trade, processing, market trends, challenges, and future opportunities.
1. Global Production of Grapes
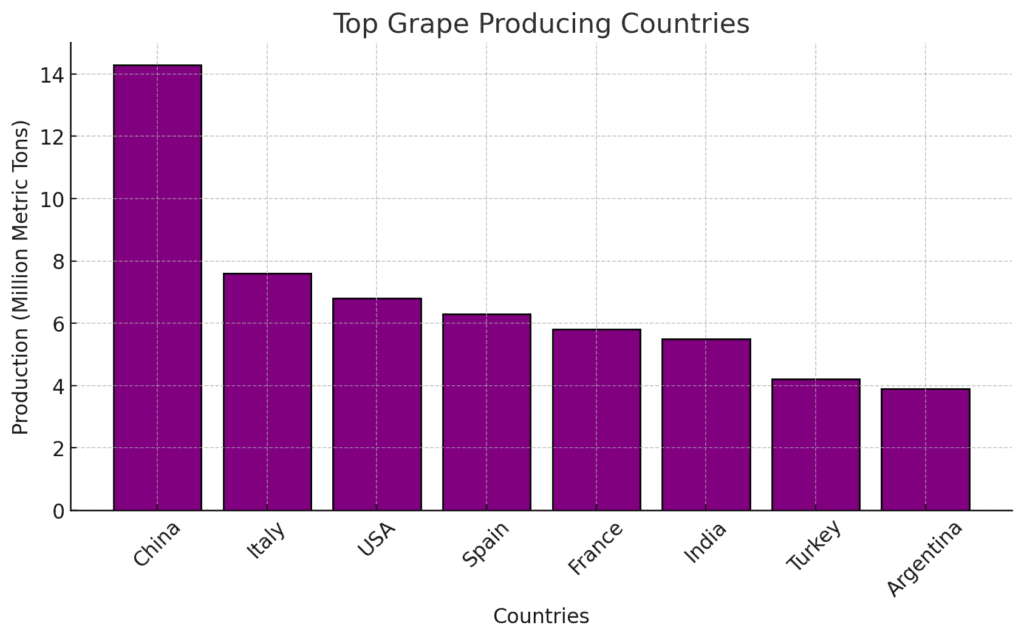
1.1 Leading Grape Producing Countries
Grape production is concentrated in key regions with optimal climate conditions. The top grape-producing countries include:
- China – The largest producer, contributing over 15% of global production.
- Italy – A leading producer known for high-quality table grapes and wine varieties.
- USA – California dominates grape production, mainly for wine and fresh consumption.
- Spain – A significant contributor to global grape and wine exports.
- France – Home to some of the world’s most prestigious wine-producing regions.
- India, Turkey, Argentina, Iran, and South Africa – Other important producers supplying both domestic and export markets.
1.2 Grape Production by Region
- Asia: China, India, and Turkey lead in grape production.
- Europe: Italy, Spain, and France dominate both table and wine grape industries.
- North America: The United States is the largest producer, followed by Mexico.
- South America: Argentina and Chile are major exporters of wine and table grapes.
- Africa: South Africa leads in grape cultivation for both fresh consumption and wine.
- Oceania: Australia is known for its premium wine production.
2. The Global Grape Trade
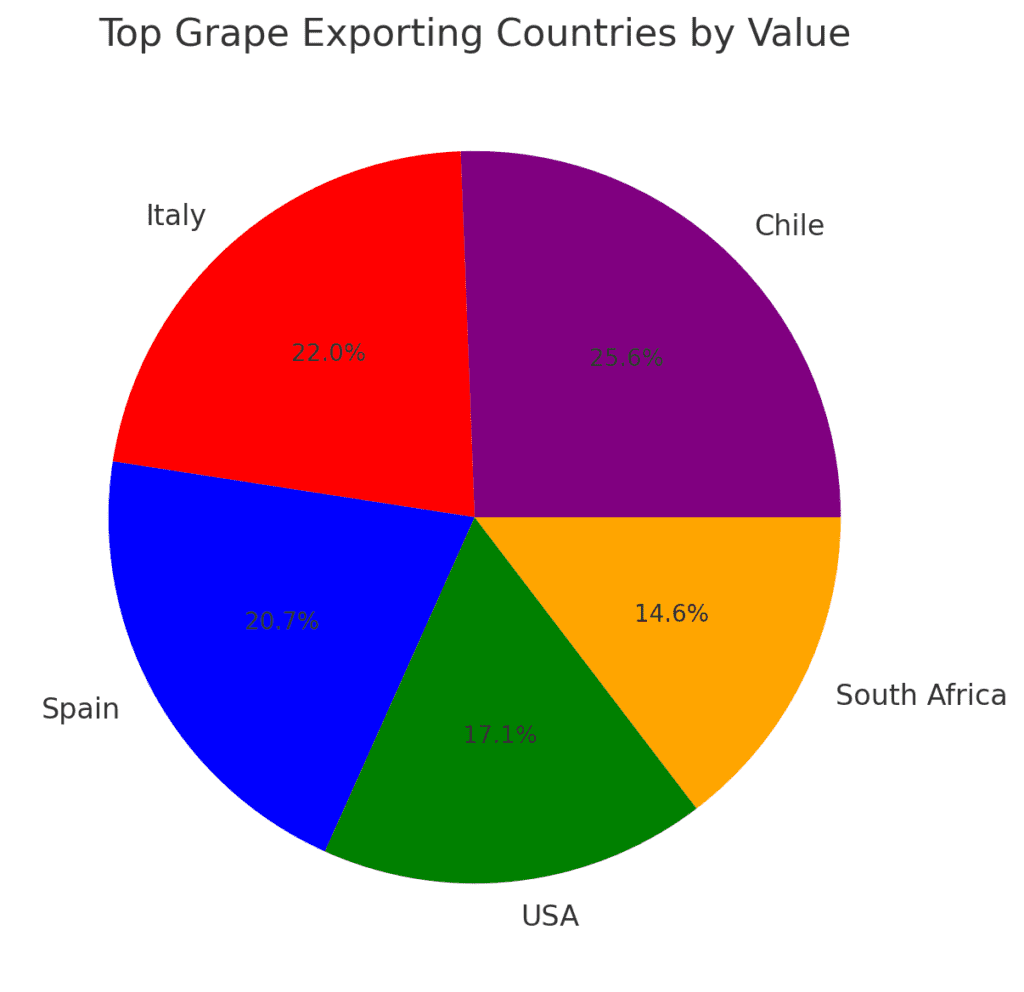
2.1 Leading Grape Exporting Countries
- Chile – The world’s largest exporter of table grapes.
- Italy & Spain – Leading exporters to the European Union and beyond.
- USA – Significant exporter to Canada, Mexico, and Asia.
- South Africa – Supplies table grapes to Europe and Asia.
- India & Turkey – Key suppliers to Middle Eastern and Asian markets.
2.2 Major Grape Importing Countries
- United States – The largest importer of table grapes.
- Germany, UK, and France – Key European markets.
- China & Japan – Growing demand for high-quality imported grapes.
- Russia & Middle Eastern countries – Increasing grape imports due to local demand.
2.3 Grape Pricing and Market Fluctuations
Grape prices vary depending on seasonality, weather conditions, supply chain disruptions, and global demand. Climate issues, such as droughts and frost, often lead to fluctuations in grape prices.
3. Grape Processing Industry
3.1 Grape-Based Products and Their Market Demand
- Wine – The most significant grape-based product, with a multi-billion dollar industry worldwide.
- Raisins & Dried Grapes – Major export products from countries like Turkey and the USA.
- Grape Juice & Concentrates – Used in beverages and food processing.
- Grape Seed Oil – Increasingly popular in cosmetics and culinary applications.
- Grape Extracts & Supplements – Used in pharmaceuticals and dietary products.
3.2 Leading Grape Processing Companies
Some of the biggest players in the grape processing industry include:
- Constellation Brands (USA) – A major global wine producer.
- E. & J. Gallo Winery (USA) – One of the largest wine and grape juice companies.
- Treasury Wine Estates (Australia) – A leader in high-end wine production.
- Pernod Ricard (France) – A multinational beverage giant producing premium wines.
4. Challenges Facing the Grape Industry
4.1 Climate Change and Environmental Impact
- Droughts & Water Scarcity – Affects grape yield in key growing regions.
- Temperature Extremes – Impact grape quality and harvesting schedules.
- Wildfires – A major threat to vineyards in regions like California and Australia.
4.2 Pests and Diseases
- Grape Phylloxera – A major pest affecting vineyards worldwide.
- Powdery Mildew & Downy Mildew – Common fungal diseases in grape production.
- Grape Vine Moth – A destructive pest in Mediterranean vineyards.
4.3 Trade Barriers and Tariffs
- EU & US Trade Policies – Affect wine and table grape exports.
- China’s Import Regulations – Influence grape trade flows.
- Sanitary & Phytosanitary Measures – Affect the movement of fresh grapes across borders.
4.4 Supply Chain & Labor Challenges
- Seasonal Labor Shortages – Impact harvesting and processing operations.
- Logistics & Shipping Costs – Increased expenses for international exports.
5. Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
5.1 Growth of Organic and Sustainable Grape Farming
- Expansion of Organic Vineyards – Increasing demand for organic wine and table grapes.
- Sustainable Practices – Use of eco-friendly farming techniques to reduce environmental impact.
5.2 Technological Innovations in Grape Farming
- Precision Agriculture – Use of AI and satellite monitoring for vineyard management.
- Automated Harvesting – Reducing labor dependency in grape harvesting.
- Genetic Improvements – Developing disease-resistant grape varieties.
5.3 Increasing Demand for Functional Grape-Based Products
- Health Drinks & Nutraceuticals – Rising demand for grape extracts in dietary supplements.
- Grape-Based Natural Sweeteners – Used as alternatives to refined sugar.
5.4 Expansion of Wine and Beverage Markets
- Emerging Wine Markets – Increased wine consumption in Asia and South America.
- Grape-Infused Alcoholic Beverages – Growth in innovative wine and grape spirits.
Conclusion
The global grape industry remains a vital part of agriculture, with diverse applications in fresh consumption, wine production, and processing industries. Despite challenges such as climate change, trade regulations, and labor shortages, the sector continues to innovate and expand. With the growth of organic farming, technological advancements, and rising global demand, the grape industry is poised for a strong future.
Sources:
- https://www.fao.org
- https://www.trademap.org
- https://www.statista.com
- https://www.oiv.int
- https://www.wineinstitute.org



