The world is facing a complex and disruptive wheat shortage in 2025. This crisis stems from a perfect storm of climate events, export restrictions, geopolitical instability, and pricing dynamics. Wheat—one of the most widely consumed and traded grains—has become a key concern for global food security, affecting both major importers and exporters. This report breaks down the causes of the current wheat crisis, the impacts across global markets, and the outlook for wheat production and trade.
🔍 Understanding the 2025 Global Wheat Shortage
1. Overview of Global Wheat Stocks
In 2025, global wheat stocks are under pressure. While India’s wheat inventories have climbed to their highest level in three years (11.8 million metric tons), global export volumes are forecasted to fall by 7.2%, hitting a three-year low. This creates a dual reality—some domestic markets show surplus, but international trade flows are constrained. The USDA estimates lower exports from key players like Kazakhstan and Russia, and declining demand from China and Turkey.
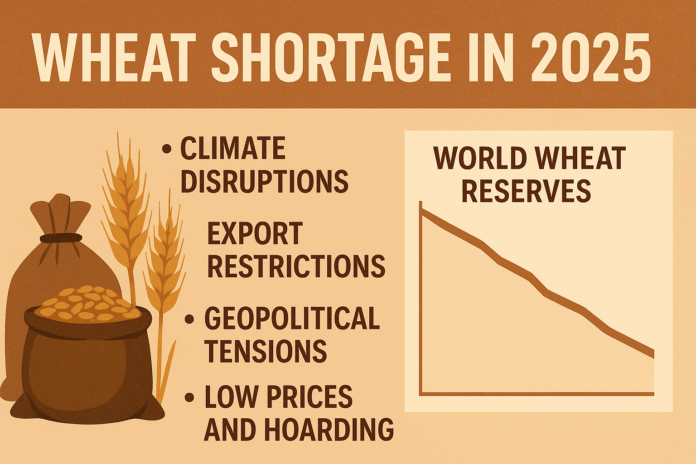
2. Key Causes Behind the Wheat Shortage
a. 🌦 Climate Disruptions
Unpredictable weather patterns have devastated harvests in key wheat-producing regions. Argentina faced severe droughts, while parts of Europe experienced excessive rainfall that disrupted planting and harvesting cycles. These anomalies have led to a significant reduction in crop yields and grain quality.
b. ⚔️ Geopolitical Tensions
The ongoing Russia-Ukraine war continues to affect exports from the Black Sea region, a major wheat supply corridor. With Ukraine and Russia historically contributing nearly 30% of global wheat exports, any disruption significantly impacts global availability and price stability.
c. 📉 Price Suppression and Farmer Hoarding
In 2024 and early 2025, wheat prices remained relatively low despite global uncertainty. Anticipating higher future prices, farmers in countries like Australia, Argentina, and Canada have delayed releasing their harvests to the market. This speculative hoarding has led to supply tightness for millers and buyers, particularly in Asia and the Middle East.
d. 🚫 Export Restrictions
In an effort to secure domestic supply, some governments have imposed export restrictions. Although not yet as widespread as during the rice crisis, these restrictions are fueling speculation and panic buying, especially in import-reliant countries.
3. Global Impact of the Wheat Shortage
a. 💰 Price Volatility
Spot prices for wheat have fluctuated sharply in early 2025, with some futures markets seeing upward pressure. However, global benchmark prices remain below 2022 peaks, indicating suppressed volatility due to stock hoarding and alternative grain substitution.
b. 🛡️ Food Security Risks
Import-dependent nations across North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, and the Middle East are vulnerable. Rising wheat prices contribute to inflation and reduce food affordability. Countries like Egypt, Bangladesh, and Yemen are already signaling concern about the affordability of wheat-based products.
c. 🔄 Changes in Crop Planning
Many farmers globally are adjusting their future planting plans. Wheat acreage may decline in 2026 in favor of more drought-resistant or high-value crops like barley, sorghum, or legumes unless price incentives increase significantly.
🔮 What to Expect Next: Projections and Policy Options
1. 📈 Global Production Forecast
The FAO expects global wheat production to rise slightly by 1% in 2025 to about 796 million tonnes. The European Union, particularly France and Germany, is expected to post higher yields, slightly offsetting declines elsewhere.
2. 🔄 Global Trade Contraction
USDA projections suggest global wheat trade volumes will decline due to decreased output from Russia and Kazakhstan and weakened demand from top buyers like China. Importers are diversifying to alternative grains like corn and sorghum.
3. 🧭 Strategic Interventions
To mitigate the crisis, the following measures are being discussed:
- Encouraging responsible release of stockpiled wheat through price supports.
- Strategic reserve utilization by importing nations.
- Export control coordination through multilateral platforms like the G20.
🧾 Conclusion
The global wheat shortage of 2025 is not defined by total production decline but by regional imbalances, climate stress, geopolitical risk, and supply chain inefficiencies. While short-term relief may come from favorable weather in Europe and India’s stronger-than-expected harvest, systemic issues—like trade volatility and climate resilience—must be addressed for long-term stability.
As wheat remains a global dietary staple, policy responses, pricing incentives, and innovation in climate-resilient farming will be critical to prevent future shortages and safeguard food security for billions.
📚 Sources and References
- India’s Wheat Stocks Highest in 3 Years
https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/indias-wheat-stocks-highest-3-years-rice-hits-record-2025-04-16 - USDA Wheat Outlook – April 2025
https://ers.usda.gov/sites/default/files/_laserfiche/outlooks/111138/WHS-25c.pdf - FAO Food Outlook March 2025
https://www.fao.org/worldfoodsituation/csdb/en/ - Flour Millers Face Wheat Supply Crunch
https://www.reuters.com/markets/commodities/flour-millers-face-supply-crunch-wheat-farmers-tighten-grip-stocks-2024-11-21 - Climate Disaster Is Reshaping Global Food Costs
https://time.com/7010929/climate-disaster-food-cost-essay/ - Economic Impact of the Russian Invasion of Ukraine (Wikipedia)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economic_impact_of_the_Russian_invasion_of_Ukraine - 2024–2025 Wheat Price Forecast – Morpher Blog
https://www.morpher.com/blog/2024-wheat-price-forecast