
Soybeans are one of the most traded agricultural commodities globally, driven by demand for animal feed, soybean oil, and biofuels. A few countries dominate the soybean export market, accounting for the bulk of global shipments. This report highlights the leading soybean exporters, their export volumes, and the global markets they serve.
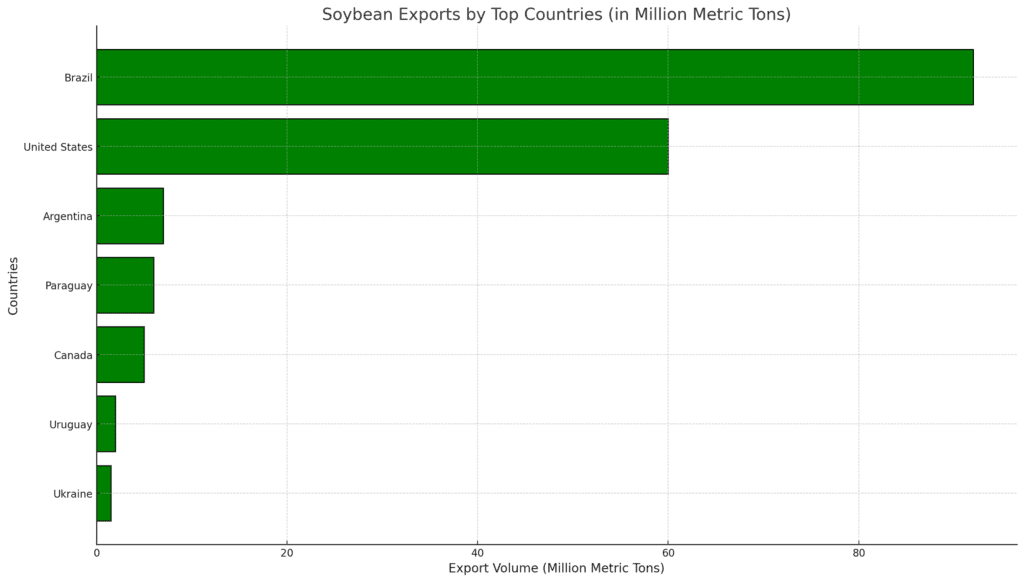
1. Brazil
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 92 million metric tons (2023).
- Global Share: Over 50% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: China (major importer), the European Union, and Southeast Asia.
- Highlights:
- Brazil’s soybean exports are supported by large-scale production, advanced logistics, and high-quality soybeans.
- Ports like Santos and Paranaguá handle the majority of Brazil’s soybean shipments.
- Sustainable farming practices are increasingly emphasized to meet international demand.
2. United States
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 60 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Around 30% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: China, Mexico, and the European Union.
- Highlights:
- The U.S. benefits from its central location, advanced farming techniques, and efficient supply chain.
- The Mississippi River plays a critical role in transporting soybeans to export terminals.
- Trade relationships with China significantly impact export volumes.
3. Argentina
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 7 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Around 4% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: China, Vietnam, and European countries.
- Highlights:
- Argentina is a major exporter of processed soybean products like soybean meal and oil.
- Its exports are constrained by domestic demand and government policies regulating export taxes.
- The Rosario Grain Port is central to Argentina’s soybean export operations.
4. Paraguay
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 6 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Around 3% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: European Union, Russia, and Asian countries.
- Highlights:
- Paraguay’s soybean exports are crucial for its economy, with most production geared for export.
- Landlocked Paraguay relies on river transport through neighboring countries like Argentina and Brazil.
5. Canada
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 5 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Around 2.5% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: China, the European Union, and Japan.
- Highlights:
- Canada exports both non-GMO and high-quality food-grade soybeans.
- Advanced farming techniques and strong trade relationships boost Canada’s position as a reliable exporter.
6. Uruguay
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 2 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Less than 1% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: China, European countries, and Vietnam.
- Highlights:
- Uruguay’s soybean industry is export-focused, benefiting from favorable trade agreements.
- Sustainable farming practices help Uruguay meet the quality standards of international buyers.
7. Ukraine
- Annual Export Volume: Approximately 1.5 million metric tons.
- Global Share: Around 1% of global soybean exports.
- Top Markets: European Union and the Middle East.
- Highlights:
- Ukraine’s soybean exports are primarily directed to neighboring countries.
- Ongoing geopolitical issues have affected production and export capacities.
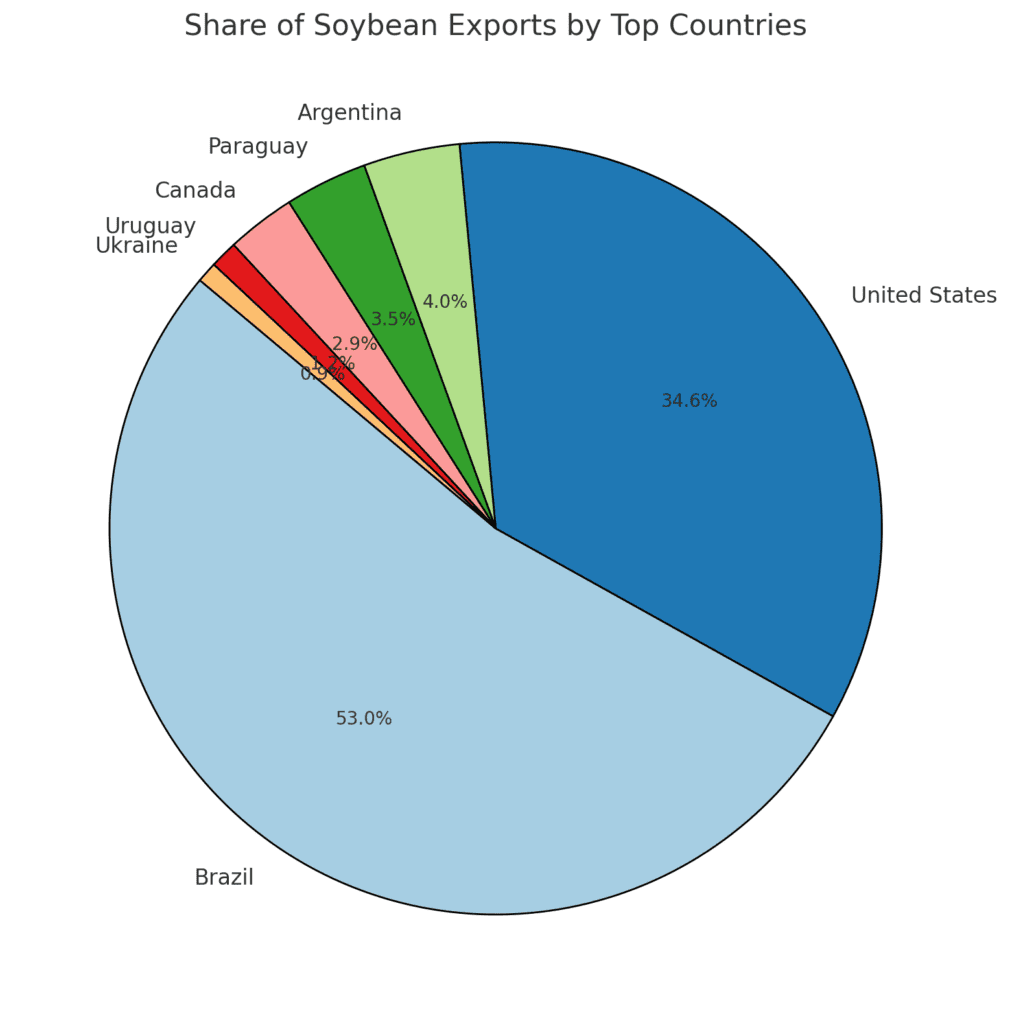
Key Drivers of Soybean Exports
- Rising Global Demand: Soybeans are in high demand for livestock feed, plant-based protein, and biodiesel production.
- Infrastructure Development: Efficient transport systems and modern port facilities play a vital role in boosting exports.
- Trade Relationships: Strong export ties with major importers like China and the European Union drive growth.
Challenges Facing Soybean Exporters
- Trade Disputes: Tariffs and trade restrictions can significantly impact export volumes.
- Climate Change: Unpredictable weather conditions affect yields and export supply.
- Logistics Constraints: Infrastructure limitations in some exporting countries can hinder smooth trade operations.
Opportunities for Growth
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Meeting international standards for deforestation-free and eco-friendly soybeans.
- Diversification of Markets: Expanding into emerging markets in Africa and Southeast Asia.
- Value-Added Exports: Increasing exports of processed soybean products like meal and oil.
Conclusion
Brazil, the United States, and Argentina dominate global soybean exports, meeting the growing demand for soybeans in major markets like China and the European Union. While challenges like climate change and trade disputes persist, opportunities in sustainability and market diversification position these countries to continue leading the global soybean trade.



